The surge in healthcare software adoption is redefining the medical field, with its momentum accelerating since 2020. According to McKinsey, telehealth services alone are now used 38 times more frequently than before the COVID-19 pandemic. This shift is further fueled by the urgent need to bridge the global healthcare workforce gap, with the World Health Organization projecting a shortfall of 11 million health workers by 2030.
Amid the increasing demand for healthcare app development, delivering precision and uncompromising quality has become more important than ever to safeguard patient safety, uphold regulatory compliance, and boost operational efficiency.
To get there, meticulous healthcare software testing plays a big role by validating functionality, securing sensitive data, optimizing performance, etc., ultimately cultivating a resilient and reliable healthcare ecosystem.
This piece delves into the core aspects of healthcare software testing, from key testing types and testing plan design to common challenges, best practices, and emerging trends.
Let’s get cracking!
What is Healthcare Software Testing?
Healthcare software testing verifies the quality, functionality, performance, and security of applications to align with industry standards. These applications can be anything from electronic health records (EHR), telemedicine platforms, and medical imaging systems to clinical decision-support tools.

What is Healthcare Software Testing?
Given that healthcare software handles sensitive patient data and interacts with various systems, consistent performance and safety are of utmost importance for both patients and healthcare providers. Unresolved defects could disrupt care delivery and negatively affect patient health as well as operational efficiency.
Essentially, this process evaluates functionality, security, interoperability, performance, regulatory compliance, etc.
The following section will discuss these components in greater depth.
Learn more:
5 Key Components of Healthcare Software Testing

5 Key Components of Healthcare Software Testing
Functional testing
Functional testing verifies whether the software’s primary features fulfill predefined requirements from the development phase. This initial step confirms that essential functions operate as intended before moving on to more complex scenarios.
Basically, it involves evaluating data accuracy and consistency, operational logic and sequence, as well as the integration and compatibility of features.
Security and compliance testing
Compliance testing plays a crucial role in protecting sensitive patient data and guaranteeing strict adherence to regulations in the healthcare industry.
Healthcare software, which often handles electronic protected health information (ePHI), must comply with strict security standards such as those outlined by HIPAA or GDPR. Through compliance testing, the software is meticulously assessed so that it meets these security requirements.
Besides, testers also perform security testing by assessing the software’s security features, including access controls, data encryption, and audit controls for full protection and regulatory compliance.
Performance testing
Performance testing measures the software’s stability and responsiveness under both normal and peak traffic conditions. This evaluation confirms the healthcare system maintains consistent functionality under varying workloads.
Key metrics include system speed, scalability, availability, and transaction response time.
Interoperability testing
Interoperability testing verifies that healthcare applications exchange data consistently with other systems, following standards such as HL7, FHIR, and DICOM. This process focuses on 2 primary areas:
- Functional interoperability validates that data exchanges are accurate, complete, and correctly interpreted between systems.
- Technical interoperability assesses compatibility between data formats and communication protocols, preventing data corruption and transmission failures.
Usability and user experience testing
Usability and user experience testing evaluate how efficiently users, including healthcare professionals and patients, interact with the software. This component reviews interface intuitiveness, workflow efficiency, and overall user satisfaction.
How to Design an Effective Healthcare Software Testing Plan?
A test plan is a detailed document that outlines the approach, scope, resources, schedule, and activities required to assess a software application or system. It serves as a strategic roadmap, guiding the testing team through the development lifecycle.
Although the specifics may differ across various healthcare software types – such as EHR, hospital information systems (HIS), telemedicine platforms, and software as a medical device (SaMD), designing testing plans for medical software generally goes through 4 key stages as follows:

How to Design an Effective Healthcare Software Testing Plan?
Step 1. Software requirement analysis
Analyzing the software requirement forms the foundation of a successful healthcare app testing plan.
Here, healthcare organizations should focus on:
- Scrutinizing requirements: Analysts must thoroughly review documented requirements to identify ambiguities, inconsistencies, or gaps.
- Reviewing testability: Every requirement must be measurable and testable. Vague or immeasurable criteria should be refined instantly.
- Risk identification and mitigation: Identify potential risks, such as resource constraints and unclear requirements, then develop a mitigation plan to drive project success.
Step 2. Test planning
With clear requirements, healthcare organizations may proceed to plan testing phases.
A well-structured healthcare testing plan includes:
- Testing objectives: Define goals, e.g., regulatory compliance and functionality validation.
- Testing types: Specify required tests, including functionality, usability, and security testing.
- Testing schedule: Establish a realistic timeline for each phase to meet deadlines.
- Resource allocation: Allocate personnel, roles, and responsibilities.
- Test automation strategy: Evaluate automation feasibility to boost efficiency and consistency.
- Testing metrics: Determine metrics to measure effectiveness, e.g., defect rates and test case coverage.
Step 3. Test design
During the test design phase, engineers translate the testing strategy into actionable steps to prepare for execution down the line.
Important tasks to be checked off the list include:
- Preparing the test environment: Set up hardware and software to match compatibility and simulate the production environment. Generate realistic test data and replicate the healthcare facility’s network infrastructure.
- Crafting test scenarios and cases: Develop detailed test cases outlining user actions, expected system behavior, and evaluation criteria.
- Assembling the testing toolkit: Equip the team with necessary tools, such as defect-tracking software and communication platforms.
- Harnessing automated software testing in healthcare (optional): Use automation testing tools and frameworks for repetitive or regression testing to improve efficiency.
Step 4. Test execution and results reporting
In the final phase, the engineering team executes the designed tests and records results from the healthcare software assessment.
This stage generally revolves around:
- Executing and maintaining tests: The team conducts manual testing to find issues like incorrect calculations, missing functionalities, and confusing user interfaces. Alternatively, test automation can be employed for better efficiency.
- Defect detection and reporting: Engineers search for and document software bugs, glitches, or errors that could negatively impact patient safety or disrupt medical care. Clear documentation should detail steps to reproduce the issue and its potential impact.
- Validating fixes and regression prevention: Once defects are addressed, testing professionals re-run test cases to confirm resolution. Broader testing may also be needed to make sure new changes do not unintentionally introduce issues in other functionalities.
- Communication and reporting: Results are communicated through detailed reports, highlighting the number of tests conducted, defects found, and overall progress. A few key performance indicators (KPIs) to report are defect detection rates, test case coverage, and resolution times for critical issues.
Learn more: How to create a test plan? Components, steps, and template

Key Challenges in Testing Healthcare Software and How to Overcome Them
Software testing in healthcare is a high-stakes endeavor, demanding precision and adherence to rigorous standards. Given the critical nature of the industry, even minor errors can have severe consequences.
Below, we discuss 5 significant challenges in healthcare domain testing and provide practical strategies to overcome them.

Key Challenges in Testing Healthcare Software and How to Overcome Them
Security and privacy
Healthcare software manages sensitive patient data, making security a non-negotiable priority. Studies show that 30% of users would adopt digital health solutions more readily if they had greater confidence in data security and privacy.
Still, security testing in healthcare is inherently complex. QA teams must navigate intricate systems, comply with strict regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, and address potential vulnerabilities.
Various challenges emerge to hinder this process, including the software’s complexity, limited access to live patient data, and integration with other systems.
To mitigate these issues, organizations should employ robust encryption, conduct regular vulnerability assessments, and use anonymized data for testing while maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
Hardware integration
Healthcare software often interfaces with medical devices, sensors, and monitoring equipment, thus, hardware integration testing is of great importance.
Yet, a common hurdle is the QA team’s limited access to necessary hardware devices, along with the devices’ restricted interoperability, which make it difficult to conduct comprehensive testing. Guaranteeing compliance with privacy and security protocols adds another layer of complexity.
To address these challenges, organizations should collaborate with hardware providers to gain access to devices, simulate hardware environments when necessary, and prioritize compliance throughout the testing process.
Interoperability between systems
Seamless data exchange between healthcare systems, devices, and organizations is critical for delivering high-quality care. Poor interoperability can lead to serious medical errors, with research indicating that 80% of such errors result from miscommunication during patient care transitions.
Testing interoperability poses significant challenges because of the complexity of healthcare systems, the use of diverse technologies, and the need to handle large volumes of sensitive data securely.
To overcome these obstacles, organizations are recommended to create detailed testing strategies, use standardized protocols like HL7 and FHIR, and follow strong data security practices.
Regulatory compliance
Healthcare software must comply with many different regulations, which also vary by region. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and damage to an organization’s reputation.
Important regulations to abide by include HIPAA in the U.S., GDPR in the EU, FDA requirements for medical devices, and ISO 13485 for quality management systems.
What’s the Cost of Healthcare Application Testing?
The cost of software testing in healthcare domain is not a fixed figure but rather a variable influenced by multiple factors. Understanding these elements can help organizations plan and allocate resources effectively.
Here, we dive into 5 major drivers that shape the expenses of healthcare testing services and their impact on the overall budget.

What’s the Cost of Healthcare Application Testing?
Application complexity
The more complex the healthcare application, the higher the testing costs.
Obviously, applications featuring advanced functionalities like EHR integration, real-time data monitoring, telemedicine capabilities, and prescription management require extensive testing efforts. These features demand rigorous validation of platform compatibility, data security protocols, regulatory compliance, seamless integration with existing systems, etc., all of which contribute to increased time and expenses.
Team size & specific roles
A healthcare application project needs a diverse team, including project managers, business analysts, UI/UX designers, QA engineers, and developers.
Team size and expertise can greatly impact costs. While a mix of junior and senior professionals may be able to maintain quality, it complicates cost estimation. On the other hand, experienced specialists may charge higher rates, but their efficiency and precision often result in better outcomes and lower long-term expenses.
Regulatory compliance and interoperability
Healthcare applications must adhere to stringent regulations, and upholding them means implementing robust security measures, conducting regular audits, and sometimes seeking legal guidance – all of which add to testing costs.
What’s more, interoperability with other healthcare systems and devices introduces further complexity, as it requires thorough validation of data exchange and functionality across multiple platforms.
Testing tools implementation
The tools and environments used for testing healthcare applications also play a critical role in determining costs.
Different types of testing – such as functional, performance, and security testing – require specialized tools, which can be expensive to acquire and maintain.
If the testing team lacks access to these resources or a dedicated testing environment, they may need to rent or purchase them, driving up expenses further.
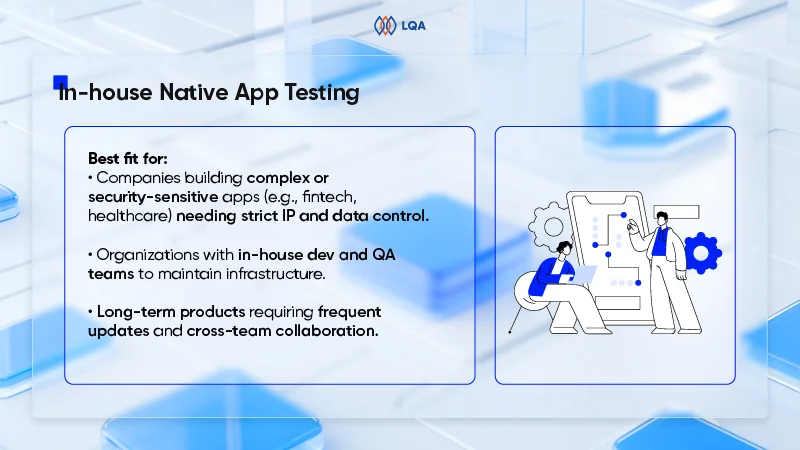
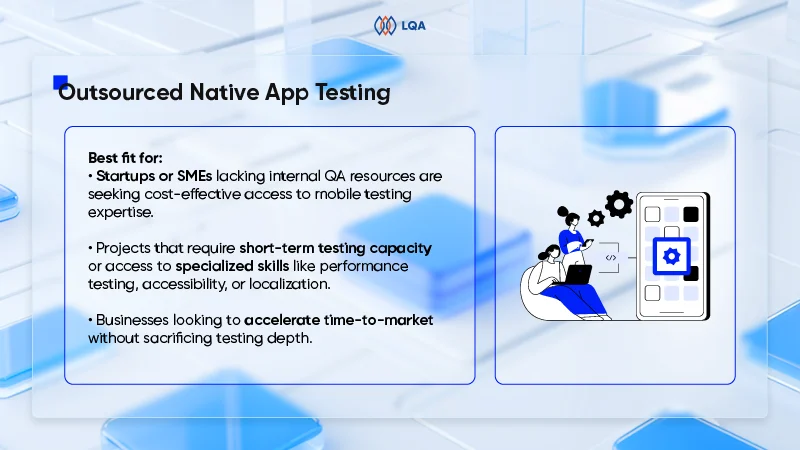
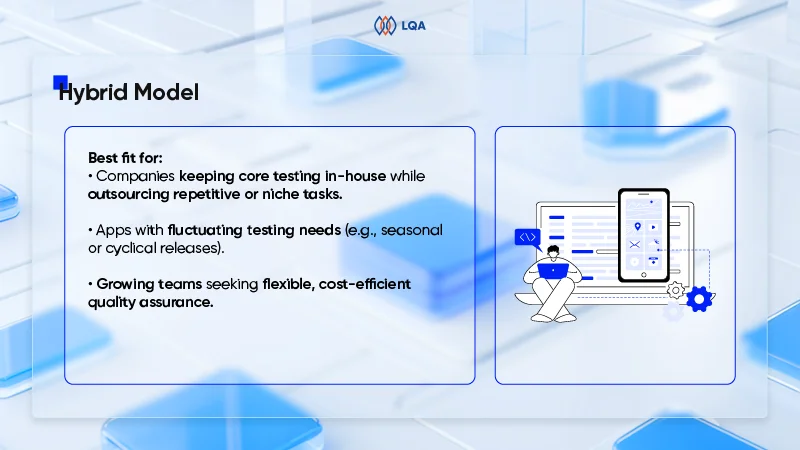
Outsourcing and insourcing balance
The decision to outsource software testing or maintain an in-house team has a significant impact on costs.
In-house teams demand ongoing expenses like salaries, benefits, and workspace, while outsourcing proves to be a more flexible and cost-effective solution. Rates of outsourcing healthcare software testing services vary depending on the vendor and location, but it often provides access to specialized expertise and scalable resources, making it an attractive option for many healthcare organizations.
Learn more: How much does software testing cost and how to optimize it?

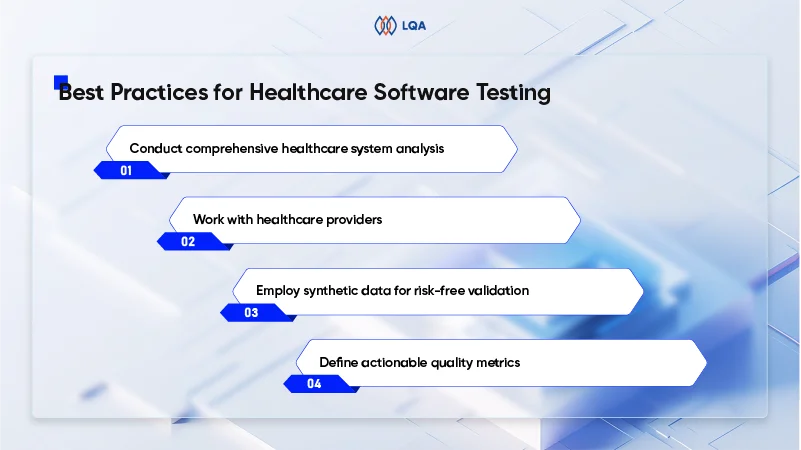
Best Practices for Healthcare Software Testing
Delivering secure, compliant, and user-centric healthcare software necessitates a rigorous and methodical approach.
Below are 5 proven strategies to better carry out healthcare QA while addressing the unique complexities of this sector.
Best Practices for Healthcare Software Testing
Conduct comprehensive healthcare system analysis
To establish a robust foundation for testing, teams must first conduct a thorough analysis of the healthcare ecosystem in which the software will operate. This involves evaluating existing applications, integration requirements, and user expectations from clinicians, patients, and administrative staff.
On top of that, continuous monitoring of regulatory frameworks, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA guidelines, is required to stay compliant as industry standards evolve. By understanding these dynamics, healthcare organizations can design testing protocols that reflect real-world clinical workflows and anticipate potential risks.
Work with healthcare providers
Building on this foundational analysis is only the first step; partnering with healthcare professionals such as clinicians, nurses, and administrators yields invaluable practical insights.
These experts offer firsthand perspectives on usability challenges and clinical risks that purely technical evaluations might overlook. For instance, involving physicians in usability testing can uncover inefficiencies in patient data entry workflows or gaps in medication alert systems.
As a result, fostering close collaboration between healthcare providers and testers and actively engaging them throughout the testing process elevates the final product quality, where user needs are met and seamless adoption is achieved.
Employ synthetic data for risk-free validation
Software testing in healthcare domain on a completed or nearly finished product often requires large datasets to evaluate various scenarios and use cases. While many teams use real patient data to make testing more realistic, this practice can risk the security and privacy of sensitive information if the product contains undetected vulnerabilities.
Using mock data in the appropriate format provides comparable insights into the software’s performance without putting patient information at risk.
Furthermore, synthetic data empowers teams to simulate edge cases, stress-test system resilience, and evaluate interoperability in ways that may not be possible with real patient data alone.
Define actionable quality metrics
To measure the performance of testing efforts, organizations must track metrics that directly correlate with clinical safety and operational efficiency. Some of these key indicators are critical defect resolution time, regulatory compliance gaps, and user acceptance rates during trials.
These metrics not only highlight systemic weaknesses but also suggest improvements that impact patient outcomes. For instance, a high rate of unresolved critical defects signals the need for better risk assessment protocols, while low user acceptance rates may indicate usability flaws.
Software Testing Trends in Healthcare Domain
The healthcare technology landscape changes rapidly, demanding innovative approaches to software testing.
Here are 5 notable trends shaping the testing of healthcare applications:

Software Testing Trends in Healthcare Domain
Security testing as a non-negotiable
Modern healthcare software enables remote patient monitoring, real-time data access, and telemedicine – exposing large volumes of sensitive patient data, such as medical histories and treatment plans, to interconnected yet often fragile systems. Ensuring airtight data protection should thus be a top priority to safeguard patient privacy and prevent breaches.
Security testing now goes beyond basic vulnerability checks, emphasizing advanced threat detection, encryption validation, and compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR. Organizations must thus thoroughly assess authentication protocols, data transmission safeguards, and access controls to find and address vulnerabilities that could jeopardize patient information.
Managing big data with precision
Modern healthcare applications process and transmit vast amounts of patient data across multiple systems and platforms. These applications are built with dedicated features to facilitate data collection, storage, access, and transfer. Consequently, testing next-generation healthcare applications requires considering the entire patient data management process across various technologies. In doing so, they must guarantee that data flows smoothly between systems while maintaining efficiency and security.
Still, comprehensive testing remains essential to verify proper data management, necessary to verify that patient data is managed properly, including mandatory tests for security, performance, and compliance standards.
Adopting agile and DevOps practices
To meet demands for faster innovation, healthcare organizations are increasingly embracing agile and DevOps methodologies.
Agile testing integrates QA into every development sprint, allowing for continuous feedback and iterative improvements. Meanwhile, DevOps further simplifies this process by automating regression tests, deployments, and compliance checks.
Expanding mobile and cross-platform compatibility testing
With a growing number of users, including patients and healthcare professionals, accessing healthcare solutions through smartphones and tablets, organizations are increasingly prioritizing mobile accessibility.
Testing strategies must adapt to this shift by thoroughly evaluating the application’s functionality, performance, and security across various devices, networks, and operating environments.
Leveraging domain-skilled testing experts
Healthcare software complexity requires testers with specialized domain knowledge, including a deep understanding of clinical workflows, regulatory standards like HL7 and FHIR, and healthcare-specific risk scenarios.
For instance, testers with HIPAA expertise can identify gaps in audit trails, while those proficient in clinical decision support systems (CDSS) can validate the accuracy of alerts and recommendations.
To secure these experts on board, organizations are either investing in upskilling their in-house QA teams or partnering with offshore software testing vendors who bring extensive knowledge in healthcare interoperability, compliance, patient safety protocols, and so much more.
Read more: Top 5 mobile testing trends in 2025
FAQs about Software Testing in Healthcare
What types of testing are often used for healthcare QA?
A comprehensive healthcare QA strategy typically involves multiple testing types. The most commonly used testing types are functional testing, performance testing, usability testing, compatibility testing, accessibility testing, integration testing, and security testing.
Which are some healthcare software examples used in hospitals?
Hospitals use various software, including electronic health records, telemedicine apps, personal health records, remote patient monitoring, mHealth apps, medical billing software, and health tracking tools, among other things.
What’s the cost of healthcare application testing?
The cost of testing healthcare software depends on application complexity, team size, regulatory compliance, testing tools implementation, and outsourcing vs insourcing. Generally, mid-range projects range from $30,000 to $100,000+.
What are some software testing trends in the healthcare domain?
Current healthcare software testing trends include security-first testing to counter cyber threats, Agile/DevOps integration for faster releases, big data management, domain-skilled talent, and mobile compatibility checks.
Partnering with LQA – Your Trusted Healthcare Software Testing Expert
The intricate nature of healthcare systems and sensitive patient data demands meticulous software testing to deliver reliable solutions.
A comprehensive testing strategy often encompasses functional testing to validate business logic, security testing to protect data, performance testing to evaluate system efficiency, and compatibility testing across various platforms. Accessibility and integration testing further boost user inclusivity and seamless interoperability.
That being said, several challenges emerge during the testing process. To encounter such hurdles, it’s important to comprehensively analyze healthcare systems, partner with healthcare providers, use synthetic data, determine actionable quality metrics, and stay updated with the latest testing trends.
At LQA, our team of experienced QA professionals combines deep healthcare domain knowledge with proven testing expertise to help healthcare businesses deliver secure, high-quality software that meets regulatory requirements and exceeds industry standards.
Contact us now to experience our top-notch healthcare software testing services firsthand.