How to Transition from Manual to Automation Testing: 6 Crucial Steps
The trend-bucking idea of how to do Automation Testing is such a tough trick to pull off that there are universal debates on whether enterprises should implement this or not, despite the undeniable benefits of this approach.
With the outlook for the optimal solutions for Quality Assurance, i.e. Testing, Automation Testing is deemed to deliver fast-paced output (thanks to the agile methodology), less time-consuming and repetitive. More importantly, human errors are also opted out with maximum percentile.
Eventually, it is all about bringing the best out of the product and customer service with bare leakage, which can result in a higher yield of Return on Investment (ROI)
Action speaks louder than words. You’ve probably known Why you should change from manual to automation testing. But how do you do it – transition from Manual Testing, a method that has long been in operation for the Quality Assurance process – to Automation Testing?
1. Devise a best-laid plan and scope for Automation Testing
Automation Testing sure does propose optimal and beneficial outcomes for the Quality Assurance process. However, be noted that Automation Testing cannot do 100% of the Testing Process. Instead, Automation Testing is another way round which is more competent and optimized.
|
“Automation in testing is a lot more than just recording a test or writing code, it takes planning and lots of other front-end tasks in order for it to be successful.” – Jim Hazen (Software Test Automation and Performance Test Alchemist)
|
Automation is indivisible from Manual Testing. Consequently, it requires project managers and other C-level officers to devise the best-laid plan and scope for the well-rounded set of information on what to automate and how to automate. For each question, viable solutions and division will be discussed as follows:
What to automate in testing?
The subject(s) of the Automation Testing process varies, depending on different criteria you are assessing.
| Criteria | What to automate |
| Frequency of Testing |
If your product offers frequent releases and feature updates to the market, it is recommended that your firm start your automation testing with smoke test and regression testing. Unit Testing, Functional Testing and Integration Testing are also important for your quick releases. If your product offers once-in-a-while releases and updates, you should put emphasis on functional testing and performance testing (i.e. load test, stress test). With automation being in process, the testing cycle speeds up in a shorter amount of time, under less influence of human intervention. |
| Technological Priority | Before rushing in any test cases of Automation Testing, you should decide on what your business or technological priority is. Anything with less priority can be put at the end of the queue so that your firm can easily focus on what is the most important features of the product. |
Automation testing is never the answer for large-scope testing. The key to success with automation testing is the scope definition and how focused it is. However, this is one of the top Automation Testing Challenges that one might tackle when implementing the method.
The smaller the scale of your test cases is, the more efficient it is to automate testing. Once scope and priority are set, the question of “What to automate?” is unveiled with bells and whistles requiring you to follow through will come in transparency.
How to automate?
Automation Testing is no rocket science, yet it takes us a long time of research and assessment to come up with the elements that answer the question of “How to automate?”

Steps to Automation Testing
- Set a target for automation testing process. In this step, you need to vest out the exact proportion for automation testing/manual testing for later assessment and report of efficiency.
- Start small with a minimum percentile of automation testing. This helps you in maintaining the application under test. With a full grasp and control of automation testing on a small scale, you can gradually go for a bigger picture.
- Categorize your test map with different test cases for different methods or functions to achieve the maximum coverage.
- Label your test cases with clarification and notes for later identification and report. With this being done, the collaboration between engineer testers is more synchronized and systematic without any communication breakdown. Everything is recorded on the system, secured with confidence.
- Regarding your target customers’ preferences and cross-browser compatibility, you need to set up a list of the viable browsers and devices for the strategic purposes of your business.
*Note: The proportion of manual and automation is the primal element to consider, before anything else.
2. Select an automation tool and frameworks
Unit testing, integration testing, regression testing is hopping abroad from manual to automated, thanks to the development of multiple tools, both open-source and commercial.
These tools appear in different shapes and sizes, each fits your needs in different ways, and one might need to consider different aspects to conclude on what to utilize in your automation testing process. These aspects include:
- What domain are you working on?
- What level of experience in automation testing does your IT team have?
- Would you like an open-source or commercial tool?
What domain?
|
Tool selection depends majorly on the domain of your application, whether the application targets a web-based application or a mobile-based application. If it is based on the web-UI application one can go for tools like selenium, QTP and if it is a mobile-based application you can go for tools like Appium, Robotium, etc.
|
The domains we are going for in this article are web-based and mobile-based applications.
- For web-based applications, the most common tool is Selenium and QTP.
- For mobile-based applications, Appium and Robotium are the most popular ones.
Level of Experience
The competence of one Automated Engineer Testers requires not only the experience with the frameworks/tools themselves but also a high level of programming skills. These skills can be Java, JavaScript, Ruby, C#, etc., whichever can work under pressure for the faster cycle of releasing feature updates.
Open-Source or Commercial Tools?
Budget deficits, or budget constraints, are of the utmost importance for businesses’ decision of whether they should hop abroad with automation testing or not.
Sometimes, the cost of these tools can make one entirely rule out automation testing, so choosing the right one helps you avoid the cumbersome procedure of complaints and distress when bumping into a roadblock later.
3. Set up Grid Infrastructure
Test Grid Infrastructure is a major cog of the machine, keeping the testing operation running smoothly and compatibly.
In general, a test grid is a testbed including a large number of devices with different browsers. The application being tested will operate in different versions, on different operating systems.
|
The more versatile and robust test grid infrastructure is, the more supportive it is for your application under test. This assures maximum compatibility, making the end-user experience as pleasant as possible.
|
Grid infrastructure can be categorized into two of the following:
| On-Premise Test Grid Infrastructure | Cloud-based Test Grid Infrastructure |
|
Real devices with direct interaction with testers are available with on-premise test grid infrastructure. With this type, the control over the devices is easier and more interactive. On the other hand, the monthly or even daily releases of new devices and OS results in heavy capital on device maintenance. The number of accessible devices is limited to their availability within the reach of the testing team. |
Cloud-based Test Grid Infrastructure is available with cross-browser testing devices. With the availability and accessibility, businesses now can acquire better coverage of hardware/software environments thanks to vast combination of devices, OS and application versions. With cloud-based tool support, there is little need for test grid maintenance, yet you are still able to obtain greater scalability. |
4. Set up Test Environment
For automation testing, Test Environment Checklist covers 4 elements of Hardware, Software/connections, Environment data, Maintenance tools/processes.
- Hardware: Both crucial and peripheral equipment is to be put into consideration.
- Software/connections: Software to be set up in a test environment is required to meet the needs of your firm.
E.g. Linux, Apache, and PHP are to be set up on a web server. MySQL is to be on the Database Server. Software also includes PHP Plugin, Database Plugin, etc.
- Environment data: Standard test datasets should be checked for availability. Test data collection for regression testing would be more effective if recorded in a Defect administration system.
- Maintenance tools: Maintenance tools in a test environment ensures the testing process with no bugs or defects.
For a well-oiled machine in automation testing, the automation tools and their configurations within the Test Environment need thorough research for smooth operation.
5. Prepare Stable Application Under Test
The Application Under Test (AUT) is the subject of the automation testing process.
As in the ever-evolving pace of Information Technology, it is not uncommon to see the frequent releases of an application within a short amount of time.
However, these feature updates are in tune with the developmental strategy of your business. To put it in other words, there is a whole planning and devising process for these updates.

Prepare for Application Under Test
In order to start automation testing from scratch, it is a must to make sure that the system under test is stable.
Being stable here does not equal limited time for product updates. Instead, the changes should lean on the pathway of the business itself, thereby opting out any trivial maintenance.
“Trivial” as it is, any change poses the threat of being the “loose screw”, which can bring the whole system and operation down due to heavy maintenance and larger investment and eventually lower ROI.
6. Schedule your Test Plan
Planning is just as important as the execution of the automated testing itself. The allocation of test plans for regression testing, unit testing, functional testing, etc. is one major factor to determine the timeline, resources needed and the actual cost of the whole process.
The test plan is to be devised by the project manager or the product owner. With years of experience in their hand, the tasks, effort, infrastructure and budget will be justly dictated to complete the automation testing project.
Automation is the upcoming trend of information technology in general and the quality assurance field in particular. As beneficial as it is, automation requires a thorough understanding of nuts and bolts of many aspects such as frameworks, tools, grid infrastructure, etc.
Too busy to single-handedly transform from manual testing to automation? Let us guide you on how to do automation testing. Contact us now for more information.
- Website: https://www.lotus-qa.com/
- Tel: (+84) 24-6660-7474
- Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/LotusQualityAssurance






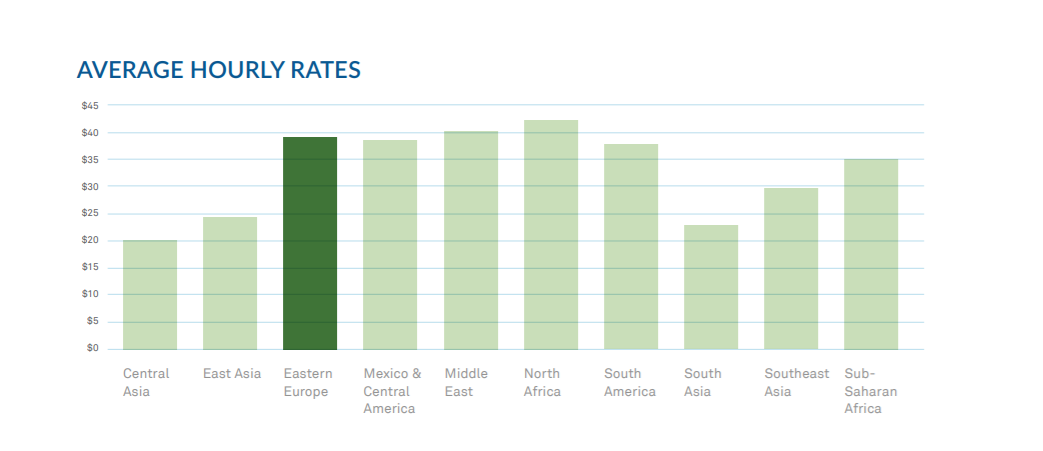
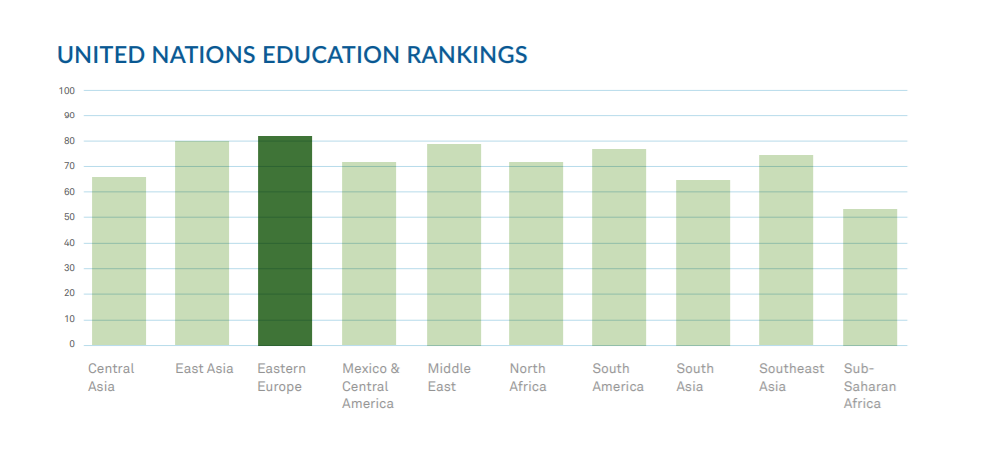
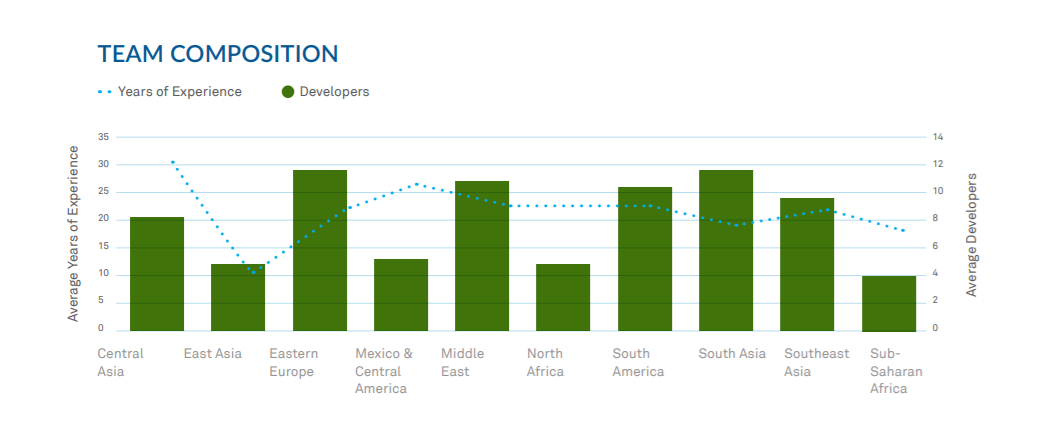 This is exacerbated by brain drain in many countries since many of the most experienced engineers may move on to other more promising regions. Eastern Europe suffered from a bit of brain drain in years past, but for the most part there are adequate opportunities available for software professionals and no need to leave to find work. The presence of so many seasoned professionals also feeds the IT ecosystem, which we’ll look into later in the report.
This is exacerbated by brain drain in many countries since many of the most experienced engineers may move on to other more promising regions. Eastern Europe suffered from a bit of brain drain in years past, but for the most part there are adequate opportunities available for software professionals and no need to leave to find work. The presence of so many seasoned professionals also feeds the IT ecosystem, which we’ll look into later in the report.