What is Functional Testing? Types and Comprehensive Guide
In today’s ever-evolving software development landscape, functional testing is critical to ensuring that software satisfies its intended specifications and functions seamlessly. Beyond only finding bugs, functional testing examines how well each component works together to contribute to the overall success of the application.
In this article, we will guide you through the comprehensive exploration of functional test, including its benefits, methodology, and how to complete a successful functional test project. Let’s get cracking!
What is Functional Testing Definition?
Functional test is a type of software testing that examines the function of a software application or system. Its main goal is to ensure that the system functions in a way that meets the business demands and conforms to the stated functional criteria.
This involves evaluating the software’s user interactions, data manipulation, input and output from the software, and how it reacts to various scenarios and conditions.
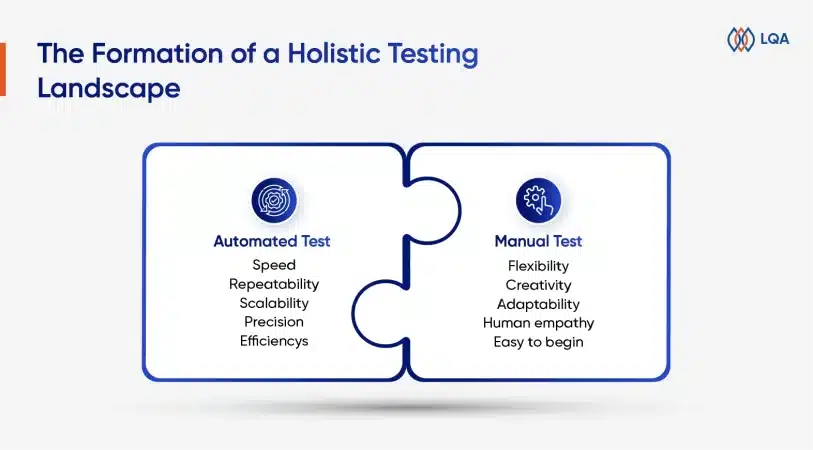
Functional vs Non-functional Testing: Key Differences
What is functional testing and non functional testing?
Functional and non functional testing are both popular and essential software testing types that help verify if a software’s features work correctly and assess aspects like performance and security for overall reliability.
The differences between functional and non-functional testing lie in their respective focuses. Functional tests focus on verifying if the required functions are met, whereas non-functional tests evaluate non-function aspects of any software such as performance, stability, efficiency, usability, visuals, etc.

Functional testing and non functional testing: Key differences
Put simply, functional test tries to answer if the software’s important functions are operating, while non-functional tests care more about how the operations occur.
What are the differences between functional and non-functional testing?
Let’s explore the key differences between functional and non-functional testing in the table below:
| Aspect | Functional testing | Non-functional testing |
| Objective | To evaluate if the software app meets functional requirements and operates as intended | To assess non-functional aspects such as usability, security, performance, and more |
| Test coverage | Typically concentrates on particular features or functions | Covers a larger range of attributes beyond functionality |
| Examples | User acceptance testing, unit testing, functional system testing, integration testing | Security testing, usability testing, compatibility testing, performance testing |
| Test criteria | Criteria for passing or failing are frequently straightforward and determined by expected results | Successful or unsuccessful criteria may include thresholds or benchmarks (for example, a response time of less than 2 seconds). |
| Tools and technologies | Some examples of functional testing tools are Selenium, JUnit, TestNG, unified functional testing (UFT), etc | Some examples of non-functional testing tools are JMeter, OWASP ZAP, LoadRunner, etc |
| Objective Measurement | Frequently has binary results (pass/fail) according to the expected behavior | Frequently uses benchmarks and quantitative measurements for non-functional attributes |
Why is Functional Testing Important?
Software functional testing is an important phase of the software development life cycle (SDLC) for a variety of reasons:

Functional testing benefits
- Verification of requirements: Functional test guarantees that the software meets the requirements. By testing each function or feature, you can ensure that the application acts as expected and meets the functional criteria.
- Bug detection: One of the key goals of functional test is to find and disclose bugs or problems in software. It aids in identifying disparities between predicted and actual results, allowing developers to correct flaws before the software is published.
- Software quality improvement: Functional testing helps to improve the overall quality of software by verifying that every module or component carries out its assigned task correctly.
- User experience optimization: Functional tests improve user experience by identifying and correcting issues early in the SDLC. It helps develop a software product that satisfies users’ expectations and reduces post-release problems.
- Cost-effectiveness: Resolving problems at a later stage of the software development life cycle or after the product has been delivered is more expensive than identifying and repairing errors early in the process. Functional test lowers the overall cost of development and maintenance by assisting in the early detection of issues.
- Risk mitigation: Functional testing assists in reducing the risks related to software development by methodically testing the program’s functioning. It gives teams information about the application’s usability, performance, and dependability so they may proactively solve any possible problems.

Streamline functional testing with LQA
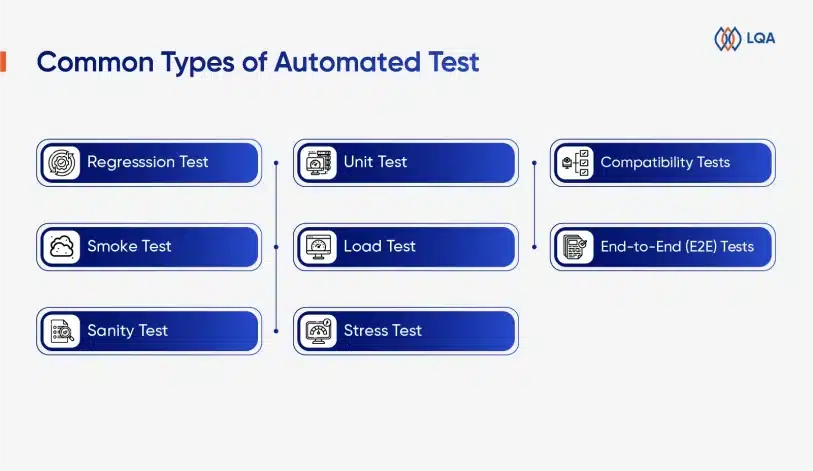
Types of Functional Testing
What are the most common functionality testing types? Here are the most common functional testing examples:

Types of functional testing
Regression testing
Regression testing ensures that new code does not break current functionality. It determines whether or not the application’s quality has deteriorated. These tests focus on the changes made and guarantee that the entire application is stable.
Unit testing
Unit testing involves breaking down the desired result into smaller units, which allows functional testers to check if a limited number of inputs, sometimes even just one, delivers the desired outcomes. By focusing on testing a specific part of the code, such as a function or method, unit testing is quick to write and run.
Integration testing
Integration testing verifies whether each software parts work properly together. This testing makes sure that the modules function properly when they are dependent on one another, even if they pass independent tests.
Smoke testing
Smoke testing is frequently used when a new build is developed. As an early-stage testing type, this method provides an additional layer of verification to determine whether the new build can move one or requires revisions.
Sanity testing
A sanity test is executed for a new build that includes small bug fixes or new code, frequently after smoke testing. This method is to verify if every major functionality of an application operates properly both on its own and in combination with others.
Usability testing
Usability testing evaluates a software product’s user interface and overall user experience and addresses usability issues. In this testing method, real users will test the product in a production environment. Their feedback will be collected for future improvements.
How to Perform Functional Tests
QA functional testing typically includes the following essential steps:

How to perform functional test?
Identify test input
Before the testing phase, quality engineers need to determine the function that needs to be tested, along with its requirements, and how it operates. This essential step allows functional testers to understand the function’s goal and learn the potential user paths.
Create test scenarios
Create a list of every potential test scenario—or at least every crucial one—that may be used for a particular feature. Test scenarios demonstrate how a feature will be used in different contexts. For example, test cases for a payment module might include different currencies, managing expired or invalid card numbers, etc.
Create test data
Based on the test scenarios that you selected, create test data that replicates typical use situations. Input the test data manually with tools like MS Excel, or automatically with a script or testing tool that retrieves data from sources such as a database, flat file, XML, or spreadsheet. Make sure that each input data has relevant information specifying the expected outcome it should produce.
Execute test cases
In this stage, the created test cases are run and the results are recorded. After that, compare the expected and real output. The actual output produced after running the test cases is compared to the predicted output to determine the level of variance in the results. This stage indicates whether or not the system is operating as intended.

Streamline functional testing with LQA
Why Automate Functional Testing?
There are various advantages of functional testing automation during the SDLC. The following are some reasons why organizations decide to automate functional testing:

Why Automate Functional Testing?
- Efficiency and speed: Automated functional test can be completed faster than manual tests. This leads to more rapid feedback on the software’s quality, which allows more frequent updates and faster release cycles.
- Reusability: Automated functional tests can be repeated without extra work and reusable at various phases of the development process. This allows consistent testing across different builds and releases, cutting down on redundancy.
- Improved test coverage: Automated functional test offers wider coverage of test scenarios and data variances. This leads to higher test coverage, ensuring that all of the application’s components are carefully tested.
In summary, automated functional test improves the software development process’s effectiveness, consistency, and dependability, which leads to better products and quicker release cycles.
Improve Your Functional Testing with LQA
Enhancing functional testing involves engaging a specialized software QA & testing firm to ensure a comprehensive evaluation and optimal testing performance.
With over 7 years of experience as the pioneering independent software QA in Vietnam, LQA stands out as a leading IT quality and security assurance organization, providing a comprehensive variety of software QA & testing services to fulfill our clients’ diversified needs.
At LQA, we stay up-to-date on the latest functional testing methodologies and employ industry-leading tools.

LQA robust software testing tools
In addition to functional tests, LQA offers full software testing services such as white box, black box, web application, mobile application, API, manual, and automation testing.
Key features of LQA’s functional test solution:
- Comprehensive software QA solutions include consultation, strategy, execution, and ongoing support.
- Ensured bug rate of less than 3% for devices, mobile, and web applications.
- Quick delivery enabled by a wide range of experienced testers.
- Optimal price-to-quality ratio, leveraging cost savings and the knowledge of Vietnamese IT professionals.
- Tailored solutions based on industry expertise.
- Maximum security assured via a Non-disclosure Agreement (NDA) and optimal security procedures during database access.
Connect with LQA’s professionals to improve your functional test experience, ensuring outstanding software quality, bug-free applications, quick project delivery, cost-effective solutions, industry-specific precision, and maximum security.

Streamline functional testing with LQA
Frequently Asked Questions About Functional Testing
1. What is functional testing in software engineering?
Functional testing is a type of software testing that aims to ensure that a software application performs as planned. It entails testing the system’s functionality by providing input and inspecting the output to ensure that the software satisfies the defined requirements and works as intended.
2. What is non-functional testing?
In contrast to functional testing, non-functional testing assesses factors including scalability, performance, usability, and dependability. Rather than focusing on particular features or functionalities, it evaluates the system’s non-functional characteristics, such as reaction time, load management, and security.
3. What is the difference between unit testing vs functional testing?
Unit testing is a type of functional testing in which the validity of individual modules or components is verified by testing them separately. More broadly, functional testing evaluates the system’s functionality as a whole.
4. What is the difference between functional vs regression testing?
Regression testing makes sure that new features don’t negatively affect already-existing functionalities, while functional test confirms that the program operates as intended. Although being one of the functional test types, regression testing focuses on potential problems with new changes, whereas functional test validates features.
5. What is the difference between functional vs integration testing?
While integration testing evaluates the connections between various systems or components, the functional test looks at specific functions on their own. Both are a component of functional testing; integration testing makes sure these features work together seamlessly, whereas functional testing concentrates on features.
Final Thoughts About Functional Testing
In conclusion, functional test is the key to ensuring software reliability and user satisfaction. Its comprehensive examination of each function not only addresses and fixes possible issues but also guarantees a seamless alignment with user expectations.
Adopting a strong functional test approach is essential since it will protect against bugs and errors in advance, and increase software dependability, and user confidence.
We hope that with our comprehensive guidelines above, you can approach functional tests with confidence, creating software that not only meets but even surpasses user expectations in functionality and performance.
If you are looking for experts in conducting function testing for your software projects, contact LQA’s expert team today for top-notch functional testing services and consultancy. Let’s ensure your software stands out for all the right reasons.










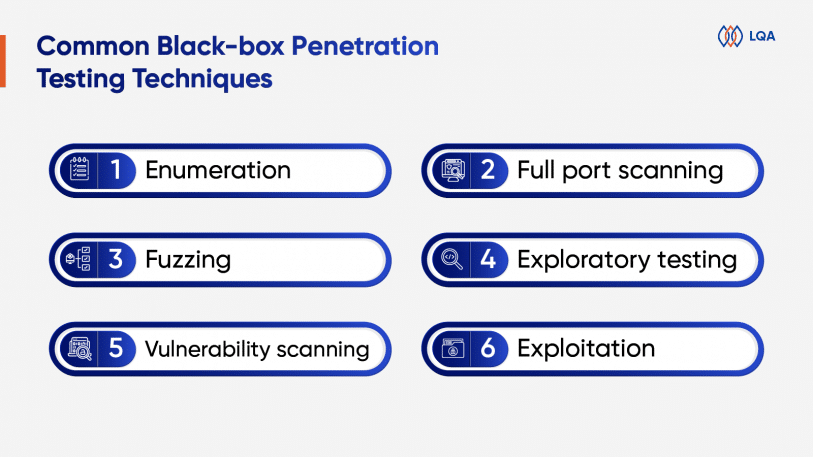 Enumeration
Enumeration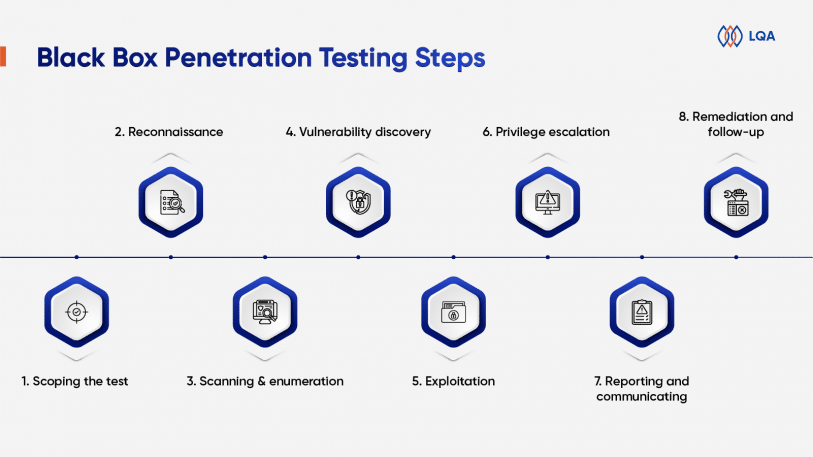 1. Scoping the test
1. Scoping the test