Software Application Testing: Different Types & How to Do?
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, application testing & quality assurance stands as crucial pillars for the success of any software product.
This article delves into the fundamentals of application testing, including its definition, various testing types, and how to test a software application.
We aim to provide a comprehensive guide that will assist you in understanding and optimizing your application testing process, ensuring the delivery of high-quality software products. Let’s get cracking!
What is Software Application Testing?
Software application testing involves using testing scripts, tools, or frameworks to detect bugs, errors, and issues in software applications.
It is a crucial phase in every software development life cycle (SDLC), helping to identify and resolve issues early on, ensuring application quality, and avoiding costly damage.

What is Software Application Testing?
According to CISQ, poor software cost the U.S. economy $2.08 trillion in 2020 alone. VentureBeat also reported that developers spend 20% of their time fixing bugs.
The costs of software bugs extend beyond the direct financial expenses that a software developer must make to fix the bugs. They lead to productivity loss due to worker downtime, disruptions, and delays. Additionally, they can harm a company’s reputation, indicating a lack of product quality to clients.
Moreover, bugs can introduce security risks, leading to cyberattacks, data breaches, and financial theft.
For instance, Starbucks was forced to close about 60% of its stores in the U.S. and Canada, due to a software bug in its POS system. In 1994, a China Airlines Airbus A300 crashed due to a software error, resulting in the loss of 264 lives.
These statistics and examples emphasize the importance of application testing. However, implementing an effective QA process requires essential steps and a comprehensive testing plan.
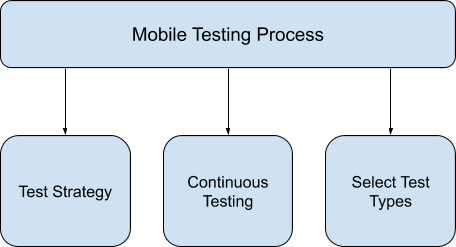
Software Application Testing Process: How to Test a Software Application?
A thorough software testing process requires well-defined stages. Here are the key steps:
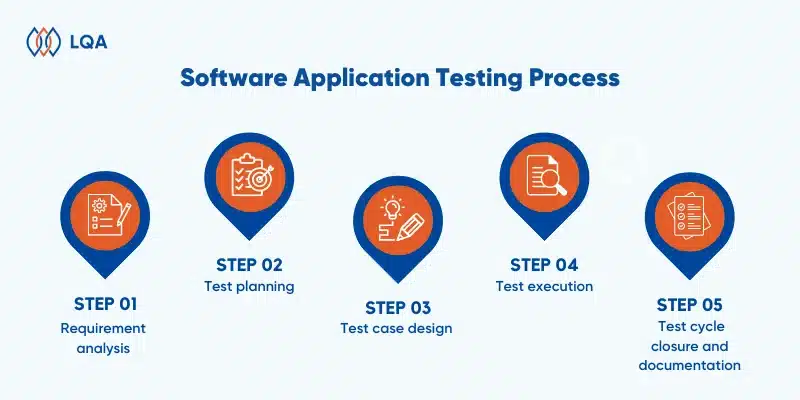
Software Application Testing Process
Requirement analysis
During this initial phase, the testing team gathers and analyzes the testing requirements to understand the scope and objectives of the testing process.
Clear test objectives are defined based on this analysis, aligning the testing efforts with the overall project goals.
This step is crucial for customizing the software testing lifecycle (STLC) and determining the appropriate testing approaches.
Test planning
After analyzing requirements, the next step is to determine the test plan strategy. Resources allocation, software testing tools, test environment, test limitations, and the testing timeline are determined during this phase:
- Resource allocation: Determining the resources required for testing, including human resources, testing tools, and infrastructure.
- Test environment setup: Creating and configuring the test environment to mimic the production environment as closely as possible.
- Test limitations: Identifying any constraints or limitations that may impact testing, such as time, budget, or technical constraints.
- Testing timeline: Establishing a timeline for testing activities, including milestones and deadlines.
- QA metrics: Determining testing KPIs and expected results to ensure the effectiveness of the testing process.
Check out the comprehensive test plan template for your upcoming project.
Test case design
In this phase, the testing team designs detailed test cases based on the identified test scenarios derived from the requirements.
Test cases cover both positive and negative scenarios to ensure comprehensive testing coverage. The test case design phase also involves verifying and reviewing the test cases to ensure they accurately represent the desired software behavior.
For automated testing, test scripts are developed based on the test cases to automate the testing process.
Test execution
Test execution is where the actual testing of the software application takes place. Testers execute the predefined test cases, either manually or using automated testing tools, to validate the functionality of the software.
Input data and various conditions are simulated during this phase to assess how the software responds under different scenarios. Any defects encountered during testing are documented and reported for further analysis and resolution.
Delve deep into testing world:
Test cycle closure and documentation
The final step involves closing the test cycle and documenting the testing process comprehensively.
A test completion matrix is prepared to summarize test coverage, execution status, and defect metrics. Test results are analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement in future testing cycles.
Comprehensive documentation of test results, defects, and testing artifacts is prepared for reference and software audit purposes. Conducting a lessons-learned session helps capture insights and best practices for optimizing future testing efforts.
Software Application Test Plan (STP)
A software application test plan is a comprehensive document that serves as a roadmap for the testing process of a software application or system. It outlines the approach, scope, resources, schedule, and activities required for effective testing throughout the software development lifecycle.
A well-crafted test plan is crucial for ensuring the success, reliability, and quality of a software product. It provides a detailed guide for the testing team, ensuring that testing activities are conducted systematically and thoroughly.
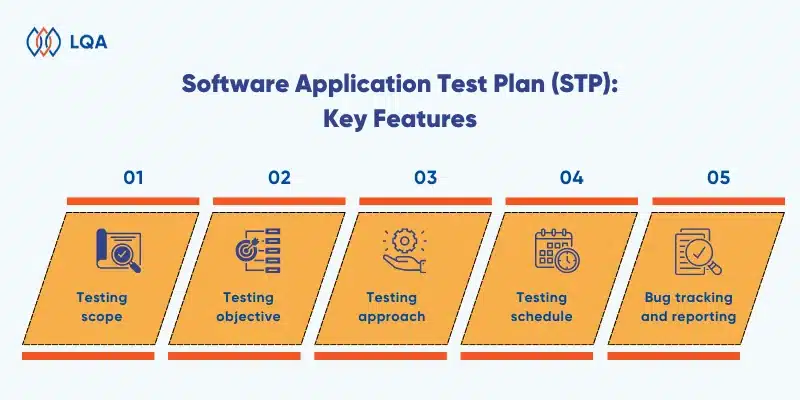
Software Application Test Plan (STP)
A standard test plan for application testing should define the following key features:
- Testing scope: Clearly define the boundaries and coverage of testing activities, including what functionalities, modules, or aspects of the application will be tested.
- Testing objective: Pinpoint the specific goals and objectives of the testing process, such as validating functionality, performance, security, or usability aspects.
- Testing approach: Outline the testing approach to be used, whether it’s manual testing, automated testing, or a combination of both. Define the test strategies, techniques, and methodologies to be employed.
- Testing schedule: Establish a detailed testing schedule that includes milestones, deadlines, and phases of testing (such as unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing).
- Bug tracking and reporting: Define the process for tracking, managing, and reporting defects encountered during testing. Include details about bug severity levels, priority, resolution timelines, and communication channels for reporting issues.
In case you haven’t created a test plan before and desire to nail it the very first time, make a copy of our test plan template and tweak it until it meets your unique requirements.
By incorporating these key features into a test plan, organizations can ensure a structured and comprehensive approach to software application testing, leading to improved quality, reduced risks, and better overall software performance.
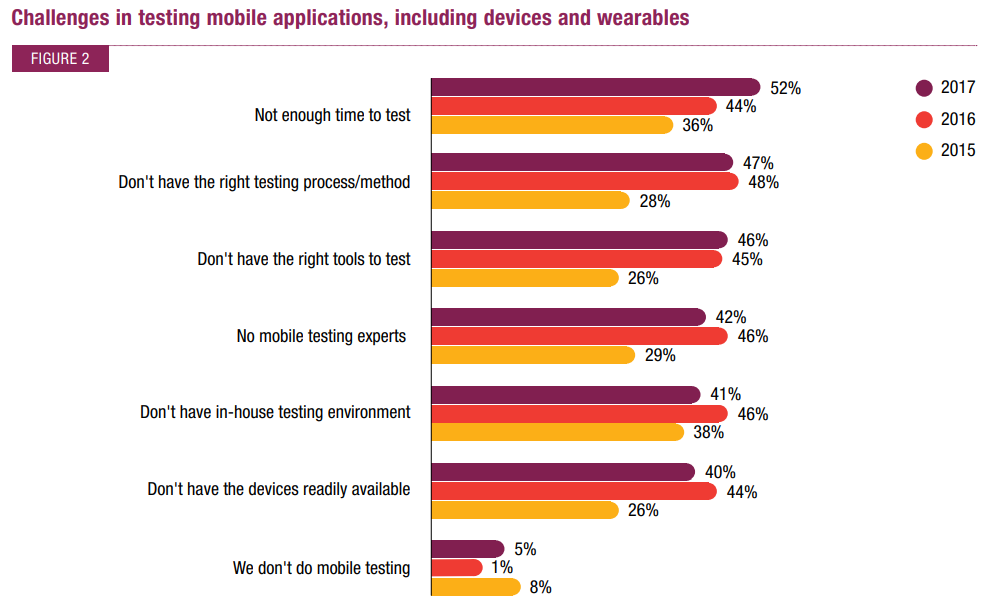
Before diving into the implementation of an application testing process, it is vital to grasp the different types of testing for a successful strategy. Application testing can be classified in various ways, encompassing methods, levels, techniques, and types. To gain a comprehensive and clear understanding of the application testing system, take a look at the infographic below.
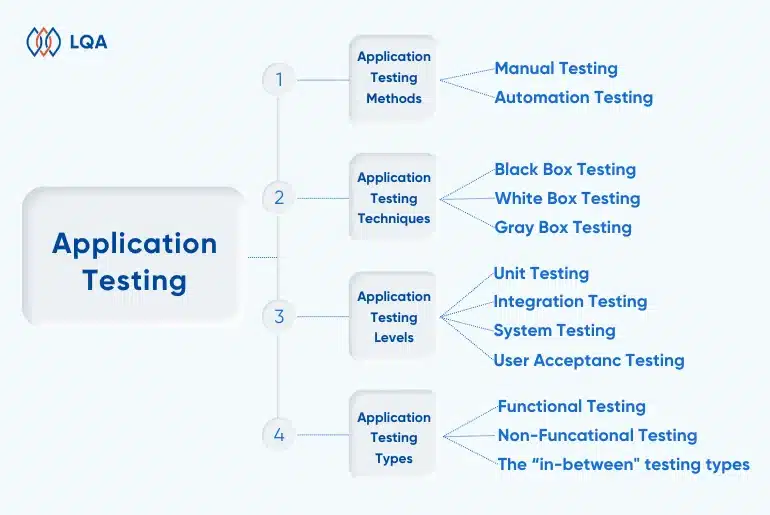
Types of testing
Application Testing Methods
There are two primary application testing methods: Manual Testing and Automation Testing. Let’s explore the key differences between Manual Testing vs Automation Testing, and understand when to use each method effectively.
Manual testing
This testing method involves human QA engineers and testers manually interacting with the software app to evaluate its functions (from writing to executing test cases).
In manual testing, QA analysts carry out tests one by one in an individual manner to identify bugs, glitches, defects, and key feature issues before the software application’s launch. As part of this process, test cases and summary error reports are developed without any automation tools.
Manual testing is often implemented in the first stage of the SDLC to test individual features, run ad-hoc testing, and assess one-time testing scenarios.
It is the most useful for exploratory testing, UI testing, and initial testing phases when detecting usability issues and user experience problems.
Automation testing
This testing method utilizes tools and test scripts to automate testing efforts. In other words, specified and customized tools are implemented in the automation testing process instead of solely manual forces.
It is efficient for repetitive tests, regression testing, and performance testing. Automation testing can accelerate testing cycles, improve accuracy, and ensure consistent test coverage across multiple environments.

Manual Test and Automation Test
Application Testing Techniques
Black box testing
Black box testing is a software application testing technique in which testers understand what the software product is supposed to do but are unaware of its internal code structure.
Black box testing can be used for both functional and non-functional testing at multiple levels of software tests, including unit, integration, system, and acceptance. Its primary goal is to assess the software’s functionality, identify mistakes, and guarantee that it satisfies specified requirements.
White box testing
White box testing, or structural or code-based testing, is the process of reviewing an application’s internal code and logic.
Testers use code coverage metrics and path coverage strategies to ensure thorough testing of code branches and functionalities. It is effective for unit testing, integration testing, and code quality assessment.
Gray box testing
Gray box testing is a software application testing technique in which testers have a limited understanding of an application’s internal workings.
The principal goal of gray box testing is to combine the benefits of black box testing and white box testing to assess the software product from a user perspective and enhance its overall user acceptance. It is beneficial for integration testing, usability testing, and system testing.
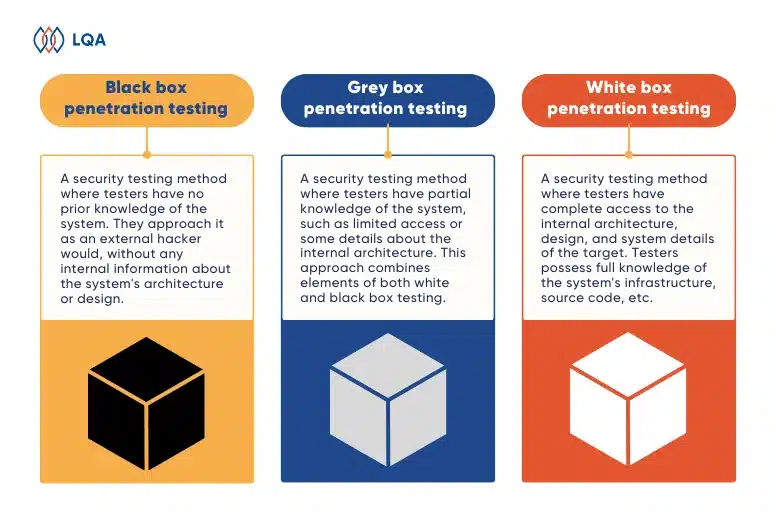
Black box, Grey box and White box penetration testing differences
Application Testing Levels
Unit testing
Unit testing focuses on testing individual units or components of the software in isolation. It verifies the correctness of each unit’s behavior and functionality. Unit testing is most useful during development to detect and fix defects early in the coding phase.
Integration testing
Integration testing verifies the interactions and data flow between integrated modules or systems. It ensures that integrated components work together seamlessly. Integration testing is crucial during the integration phase of SDLC to identify interface issues and communication errors.
System testing
System testing evaluates the complete and fully integrated software product to validate its compliance with system specifications. It tests end-to-end functionality and assesses system behavior under various conditions. System testing is conducted before deployment to ensure the software meets user expectations and business requirements.
User acceptance testing
User acceptance testing (UAT) ensures that the software meets user expectations and business requirements. It involves real-world scenarios and is conducted by end-users or stakeholders. Acceptance testing is often conducted in the final stages to ensure alignment with user expectations, business goals, and readiness for production deployment.
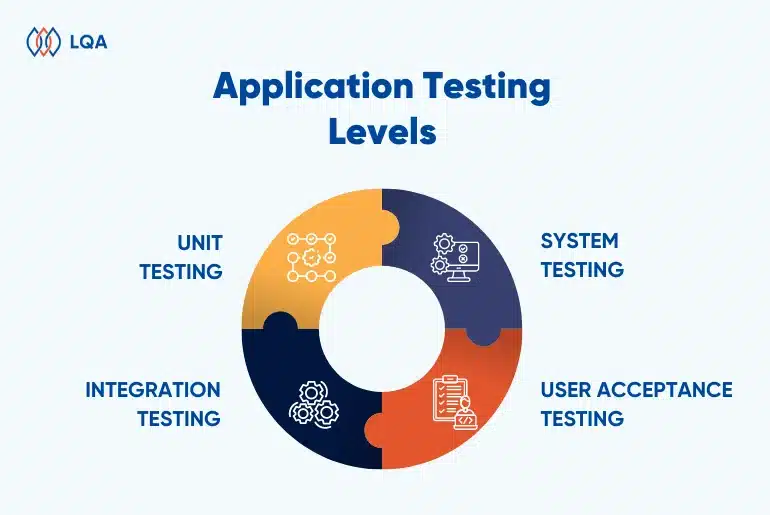
Software application testing levels
Types of Software Application Testing
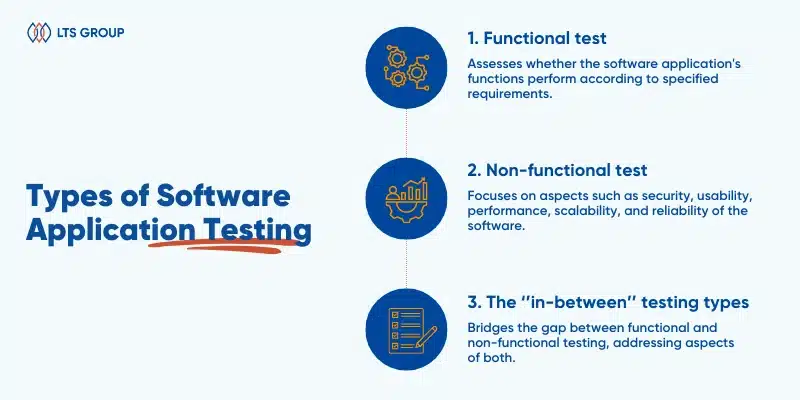
Software application testing types
Functional test
Functional testing assesses whether the software application’s functions perform according to specified requirements. It verifies individual features, input/output behavior, and functional workflows.
Some common functional test types include:
- Compatibility testing: Verifies the software’s compatibility across different devices, operating systems, browsers, and network environments to ensure consistent performance and functionality.
- Performance testing: Assess the software’s responsiveness, scalability, stability, and resource utilization under varying workloads to ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction.
- Security testing: Identifies vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and potential security risks within the software to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats.
- GUI testing: Focuses on verifying the graphical user interface (GUI) elements, such as buttons, menus, screens, and interactions, to ensure visual consistency and proper functionality.
Non-functional test
Non-functional testing focuses on aspects such as security, usability, performance, scalability, and reliability of the software. It ensures that the software meets non-functional requirements and performs well under various conditions and loads.
Some common non-functional testing types implemented to ensure robust and user-friendly software include:
- API testing: Validates the functionality, reliability, and performance of application programming interfaces (APIs) to ensure seamless communication and data exchange between software components.
- Usability testing: Evaluates how user-friendly and intuitive the software interface is for end-users, focusing on ease of navigation, clarity of instructions, and overall user experience.
- Load testing: Assesses how the software performs under high volumes of user activity, determining its capacity to handle peak loads and identifying any performance bottlenecks.
- Localization testing: Verifies the software’s adaptability to different languages, regions, and cultural conventions, ensuring it functions correctly and appropriately in various local contexts.
- Accessibility testing: Ensures the software is usable by people with disabilities, checking compliance with accessibility standards and guidelines to provide an inclusive user experience.
- Penetration testing: Simulates cyberattacks on the software to identify security vulnerabilities, assessing its defenses against potential threats and breaches.
The ‘’in-between’’ testing types
In software development, several testing types bridge the gap between functional and non-functional testing, addressing aspects of both. These “in-between” testing types include:
- Regression testing: Checks for unintended impacts on existing functionalities after code changes or updates to ensure that new features or modifications do not introduce defects or break existing functionalities.
- Integration testing: Examines the interactions between integrated modules or components of the software, ensuring they work together as intended and correctly communicate with each other.
- System testing: Evaluates the complete and integrated software system to verify that it meets the specified requirements, checking overall functionality, performance, and reliability.
- User acceptance testing: Involves end-users testing the software in real-world scenarios to confirm it meets their needs and expectations, serving as the final validation before release.
Best Practices for Application Testing with LQA
With over 8 years of experience and being the pioneering independent software QA company in Vietnam, LQA is a standout entity within the LTS Group’s ecosystem, renowned for its expertise in IT quality and security assurance. We provide a complete range of application testing services, including web application testing, application security testing, mobile application testing, application penetration testing, etc.

LQA software quality assurance awards
With LQA, you can have the best practices in creating and implementing diverse types of application testing tailored to your business’s requirements. We stand out with:
- Expertise in industries: Our specialized experience, validated by awards like ISTQB, PMP, and ISO, ensures efficient and exceptional outcomes.
- Budget efficiency: Leveraging automation testing solutions, we deliver cost-effective results, benefitting from Vietnam’s low labor costs.
- TCoE compliance: Aligning with the Testing Center of Excellence (TCoE) framework optimizes QA processes, resources, and technologies for your project.
- Abundant IT talent: Our diverse pool of testers covers various specialties including Mobile and web app testing, Automation (Winform, Web UI, API), Performance, Pen Test, Automotive, Embedded IoT, and Game testing.
- Advanced technology: Leveraging cutting-edge testing devices, tools, and frameworks, our team guarantees the smooth operation of your software, delivering a flawless user experience and a competitive market advantage.

LQA robust software testing tools
LQA recognizes the crucial role of software quality testing in delivering top-tier software products. Our expertise and advanced testing methods enable businesses to attain robust, dependable, and high-performing software applications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Application Testing
What is application testing?
Application testing refers to the process of evaluating software applications to ensure they meet specified requirements, perform as expected, and are free from defects or issues.
What does an application tester do?
An application tester is responsible for designing and executing test cases, identifying bugs or defects in software applications, documenting test results, and collaborating with developers to ensure issues are resolved.
Why is application testing required?
Application testing is required to verify that software functions correctly, meets user expectations, operates efficiently, and is reliable. It helps identify and address bugs, errors, and performance issues early in the development lifecycle, leading to higher-quality software.
What is computer application testing?
Computer application testing, also known as software application testing, is the process of testing software applications to validate their functionality, performance, security, usability, and other quality attributes on computer systems.
How to test a software application?
Testing a software application involves various stages such as requirement analysis, test planning, test case design, test execution, and test cycle closure. It includes manual testing where testers interact with the application and automated testing using testing tools and scripts to validate its behavior under different scenarios.
Final Thoughts About Software Application Testing
Quality assurance through rigorous application testing processes is the keystone that ensures software products meet user expectations, function flawlessly, and remain competitive in the market.
At LQA, we understand the paramount importance of software quality testing in delivering top-notch software products. Our testing services are designed to cater to diverse testing needs, including functional testing, performance testing, usability testing, and more. By leveraging our expertise and cutting-edge testing methodologies, businesses can achieve robust, reliable, and high-performing software applications.
Investing in thorough application testing is not just a best practice; it’s a strategic imperative. If you are looking for application testing experts to optimize your testing processes and ensure top-notch software quality, do not hesitate to contact our experts at LQA. Let us partner with you on your journey to delivering exceptional software solutions that exceed expectations.