Three common challenges in Mobile Application Testing
The booming of the smartphone has opened the door for global businesses to interact with consumers more effectively and frequently through thousands of applications. Since mobile apps became a significant channel to connect with consumers, executives of firms have spent more effort on enhancing the quality of applications. However, firms have to face many mobile application testing challenges.
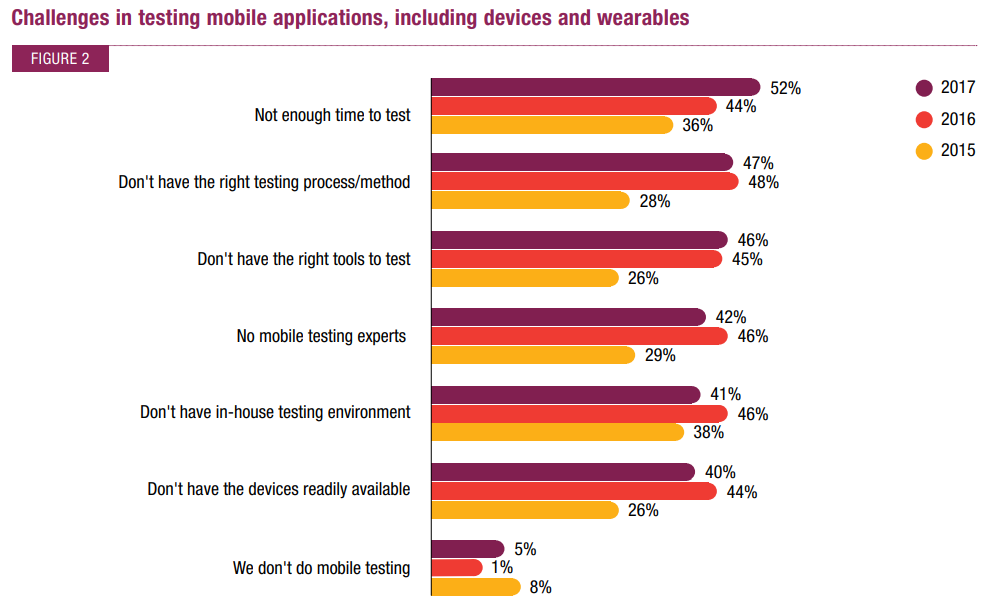
According to a report of Capgemini about Quality Assurance and Testing in 2017-18, 47% of the respondents stated that they lack an appropriate testing process or method. Meanwhile, 46% of the companies surveyed don’t know which are the right tools to perform mobile testing. Shortage in testing devices is also a crucial issue that occupies 40%.
3 Common mobile application testing challenges
1. Lack of efficient testing process
What is the effective testing process for mobile applications in such a high-competitive market like smartphone apps? There are three factors you need to consider, let’s take a look at them below:
Test Strategy
A thorough strategy for your testing project is significant. Some of the aspects that you should plan are Test methodology, Automation testing, and Test environment.
Firstly, when it comes to testing methodology, one of the most favored ones is the Agile approach. In Agile, the development process breaks into repetitive loops, and testing goes in parallel with development.
The second factor you should think about is how to set up the test environment. You can choose from setting up on real mobile devices, on simulators, or clouds.
The final thing is automation testing. Although test automation can reduce the time and effort to perform repetitive test cases such as regression testing; some of the tests still need to be run manually. One of the efficient ways to apply automation test is when you run one test case on various devices, like in this video: [Demo video] Automation test on 10 mobile devices at the same time
Continuous Testing
Mobile applications are built and updated regularly. As a result, traditional manual testing cannot keep up with the pace of releasing new versions. Continuous testing will run automation tests regularly to get immediate feedback after new updates are released. Moreover, testing apps in parallel with the development process will decrease the risk of failing at the end of the project.
Select Test Types
For mobile application testing, you should execute both functional and non-functional tests. Functional testing includes testing the function of the apps (path testing, boundary values, data lifecycle), application lifecycle, network, and display. Non-functional testing requires testers to perform some special testing, such as: Typical Interrupts Testing, Testing for Power Consumption, Testing for Different Displays, Testing for Device Input Sensors, and Testing for Screen Orientation Change.
2. Choosing from numerous testing tools
What makes mobile testing more complicated is the complexity of mobile testing tools in the market. Each tool has different features that can test a certain type of mobile apps. Companies have to know exactly what they are looking for in the testing tool to choose the one that has appropriate features, such as:
- Fees: Open-source tools and paid tools
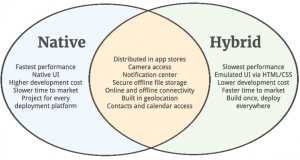
- Type of application that the tools can test: Native apps, Web, hybrid apps
- The operation system: iOS, Android, Windows
3. Shortage in testing devices
In 2019, the shipment of smartphones around the world reached 1,375 billion units, in which Android devices accounted for 76% market share and iOS devices took 13%. Each operating system has various versions, which means mobile apps have to run in numerous environments. This leads to obstacles in setting up mobile testing devices because the testing team cannot access all types of devices available. The solution is you can combine using different test environments such as Real Devices, Emulators / Simulators, and Clouds to perform testing. Each type has its advantages and drawbacks:
|
Environment |
Advantages |
Drawbacks |
| Real devices |
|
|
| Emulators |
|
|
| Clouds |
|
|
Nevertheless, the quality assurance team cannot guarantee that if a tested application works well on a given device, it will work 100% on another device. Even though it’s from the same product family, the screen resolution, CPU, Memory, and hardware could be different.
If you want to have more advices about how to improve the efficiency of mobile application testing, you can contact us for a mobile application testing service