Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe Software Tester Salary Guide 2021
Singapore, Vietnam, Malaysia and Indonesia are the centers for technology and software development in Southeast Asia. Therefore, software testing engineers are one of the most in-demand position. This report will be helpful for managers who want to figure out the differences of a tester’s salary in these countries.
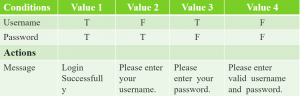
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]1. Software Testing Salary Range
Software testing salary range in Southeast Asia
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”18310″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Among the four countries, Singapore has the highest payment range for software testers. On average, testers will receive $5100 per month. The maximum salary that one can be paid is $7980; meanwhile, the minimum is $2660. Malaysia stands in the second position in terms of payment. However, its maximum amount of payment is almost four-time less than Singapore’s. The minimum, average and maximum salary of Malaysian testers consecutively are $690, $1270, and $2030. Of the four representative countries, Vietnam has the lowest salary range. It only costs the manager $330 to $2000 per month to hire a software tester here. The average salary of a Vietnamese is $650, which is three-time less than Singaporean. Nevertheless, the maximum payment for the job is almost equal to Malaysia and higher than in Indonesia. In one month, Indonesian testers can get $360 for the lowest, $720 for the medium, and $1120 for the highest payment.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space height=”30px”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Software testing salary range in different regions
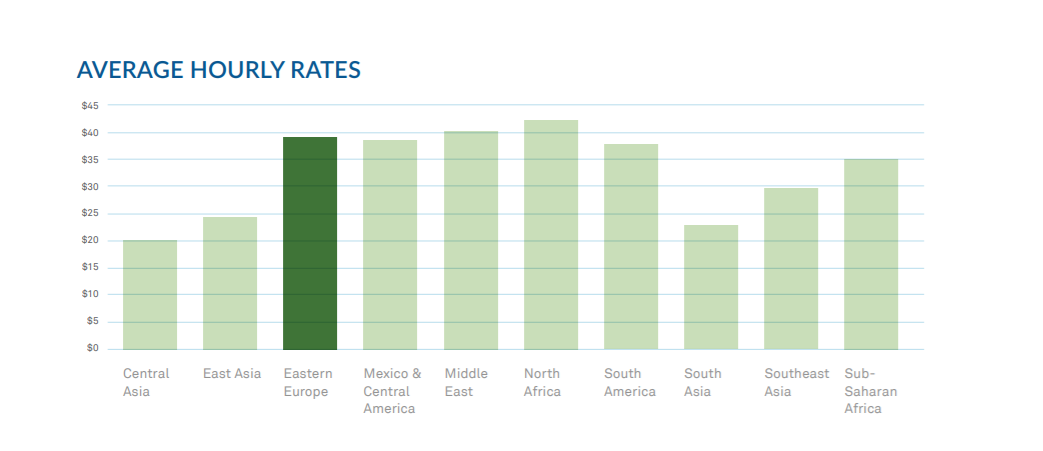
As seen in the chart above, remote team pricing is broken out into two tiers: Asia and everywhere else. In Asia, the average hourly rate is $24.62/hour, whereas the rest of the world commands higher prices averaged out around $38.67/hour.
A decade ago, there was a 400% difference in pricing from the lowest-priced region to the highest-priced region. Now the range has been cut in half. This ever-narrowing range of prices supports SourceSeek’s guiding principle that the global software market is an efficient one with enough demand to bring consistent pricing that is affected by a small set of characteristics such as location, language skill, proximity, etc.
Outliers are rare. As teams in Eastern Europe slowly set their rates higher and higher, there is enough demand to raise rates in less competitive regions accordingly and still remain competitive. The notable exception is India, where pricing trails the worldwide market due to the sheer volume of supply combined with ongoing reputation issues. There is increasing evidence that China is also beginning to see a similar trend, and will continue to have difficulty entering the global software market.
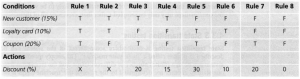
2. Software Testing Salary Based on Seniority
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Junior Software Tester Salary
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”18315″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Junior software testers often have less than two years of experience. Within this level, Singaporean testers get paid the most with $3200 per month. It quadruples the salary of a Malaysian tester, who is paid $780. Ranking in third place, Vietnam has a monthly payment of $690, fewer than the second-place $88. The country having the lowest payment for a junior software tester is Indonesia, with $570 a month. It is five-time less than Singapore.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space height=”15px”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Senior Software Tester Salary
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”18319″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]If a tester is promoted to a higher level, their salary will be increased. The monthly salary of a QA engineer in Singapore will rise by $1700 to reach $4900. Meanwhile, the salary of a senior tester in Malaysia ranks second place at $1050 per month. Receiving $180 fewer is a Vietnamese tester with a payment of $870. Indonesian tester’s salary is the lowest, which takes employers $770 per month.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space height=”15px”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Software Testing Lead Salary
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”18321″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]To hire a software testing lead, an employer has to pay $6400 per month in Singapore. The figures in Vietnam, Malaysia, and Indonesia representatively are $990, $1460, and $1060. It is noticeable that Vietnam is the one who has the lowest salary, where the tester gets a sixth-time fewer than the highest payment.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space height=”15px”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Head of Software Testing Salary
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”18320″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]The salary of the Head of software testing in Singapore is significantly high compared with the other three countries. Tester at this level will be paid $7900 a month, four-time higher than a tester on the same level in Malaysia. Vietnamese and Indonesian testers monthly income are both in the range of $1300, but Indonesian man gets extra $60 which makes Vietnam the lowest pay country for this position.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_empty_space height=”30px”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
3. Salary Based on Education
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”18322″ img_size=”full” alignment=”center”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]All four nations show a similar pattern in the chart, which is they will pay a higher salary for tester having higher education level. Besides, with the same degree, testers in Singapore get paid drastically higher than the rest. A tester who holds a certificate or diploma will gain $2660 a month in Singapore, which is eight-time higher than Vietnam and Indonesia, and a fourth-time higher than Malaysia. If the tester gets a bachelor’s degree, he or she will be paid $5100 in Singapore. This number is one-fifth in Malaysia ($1270), $720 in Indonesia, and $650 in Vietnam. Singaporean master’s degree owner will be paid $7980 a month, following by Malaysian and Vietnamese who get $2030 and $2000 representatively. The lowest-paid master’s degree holder is an Indonesian software tester, who gets $1120 per month.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]Although there are other countries in South East Asia, the four nations above are representative of the information technology center. Through the article, we showed general guidance of software tester’s salary in Singapore, Vietnam, Malaysia, and Indonesia. All the figures are collected from reliable sources, including Persol Kelly, Michael Page, and First Alliances. Hopefully, the article can be a reference when managers make their decision to hire a software tester. Nevertheless, if managers face difficulties in recruitment, there are still other alternatives such as purchasing software testing outsourcing services.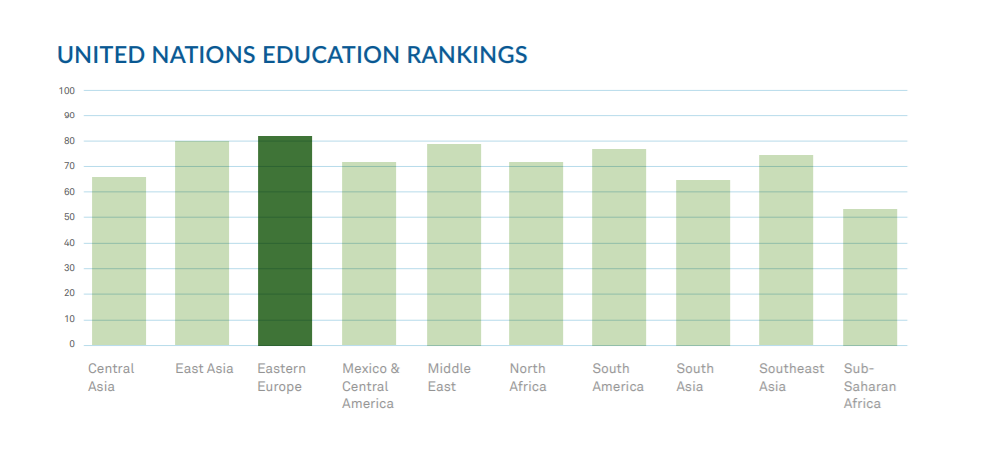
With a score of 82, Eastern European countries garnered the highest score of any region featured in this report and just edged out East Asia with a score of 80. Eastern Europe has an established reputation for having a mature and robust educational system, and many vendors in the region leverage that reputation to claim that the ‘best developers in the world’ come from Eastern Europe.
Eastern European educational excellence is focused primarily around math and science. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), which measures 70 countries in reading, math, and science, found that Eastern European countries outperformed other countries featured in this report by an average of 11% in math and 10% in science.
So, while the much-touted claim of ‘best developers in the world’ may be a bit strong, Eastern Europe’s reputation for strong education is well supported by data. While a strong general education is certainly important for a successful IT education, a high score in the UN data doesn’t always result in top IT education, and vice versa.
4. Team composition
Average years of experience is a very informative metric when assessing the maturity of a region as a whole. It takes many years for developers to gain experience and move into management and leadership, making truly senior software engineers difficult to find.
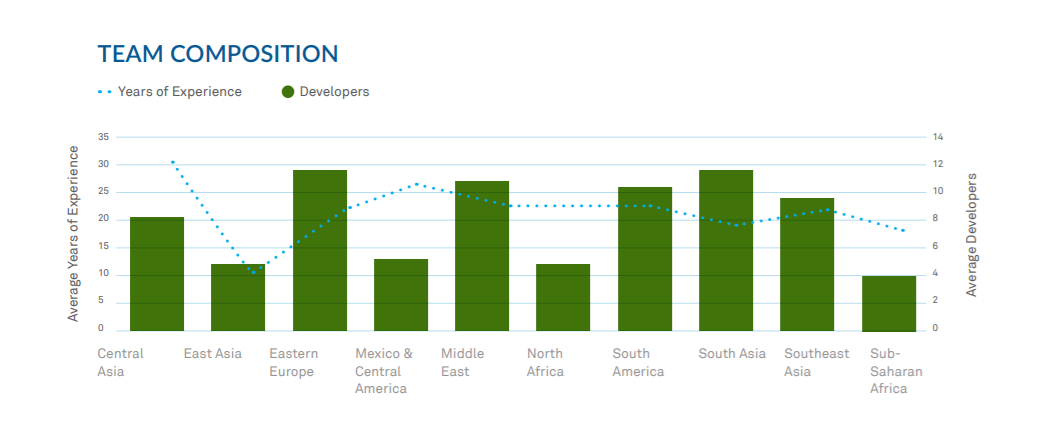 This is exacerbated by brain drain in many countries since many of the most experienced engineers may move on to other more promising regions. Eastern Europe suffered from a bit of brain drain in years past, but for the most part there are adequate opportunities available for software professionals and no need to leave to find work. The presence of so many seasoned professionals also feeds the IT ecosystem, which we’ll look into later in the report.
This is exacerbated by brain drain in many countries since many of the most experienced engineers may move on to other more promising regions. Eastern Europe suffered from a bit of brain drain in years past, but for the most part there are adequate opportunities available for software professionals and no need to leave to find work. The presence of so many seasoned professionals also feeds the IT ecosystem, which we’ll look into later in the report.
Lotus Quality Assurance is the first independent software testing company in Vietnam. As a Silver Partner of ISTQB, we provide you a talented team of testing with international experiences. Contact us to be aided with your software testing project.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]