How much does Fintech app development cost?
Fintech is a must-have feature for a business to adapt to the 4.0 world. With a good fintech app, for example, a business can pursue and engage more customers. But due to a lack of experience and expertise in technology, businesses don’t know how much does fintech app development cost. Let’s find out.
To get a thorough understanding of fintech app development costs, you should consider all of the following things:
- What features to include in fintech app development process?
- The requirements to build a good fintech app
- What is the cost for fintech app development?
1. What features to include in fintech app development process?
To successfully build a well-rounded fintech application that would attract customers, the creators have to contemplate many features and alleviate them. Mediocre features and obsolete solutions are out of the question. With a fintech app, it takes more than fancy design to attract customers. Take a look at what features you should consider for your upcoming fintech app here.
UI/UX designs for fintech app development
UI/UX design for a fintech app requires specific elements that developers and designers have to pay great attention to. These days, app users highly appreciate the application that can them freedom in how they can customize the app interface. This can make the fintech app their virtual space. The sense of belonging and ownership is considered the deciding factor for users to come back and continue to use the application.
The user-friendly interface is another must-have factor that needs to be included in your planning. Especially for youngsters, an user-friendly, clean interface is what they prefer. Chic and modernized designs are always more fascinating than those that are outdated.
More importantly, with financial operations in the app, the developers have to put simplify and visualized data in. For fintech app users, numbers, charts and graphs with in-depth analytics are what they are really looking for. Imagine a banking app with no visual reports on how the money flows, it will lack a crucial feature when compared to other applications.
Basic functionality of banking sector
An enhanced fintech app can’t be a fintech app if it lacks the basic functionality of the finance and banking sector. These functions are the must-have for your fintech app to survive among thousands of other applications. Without these basic functions, your app won’t have the chance to compete with other well-rounded apps.
The basic functions of the finance and banking sector should include:
- Account management
- Balance checking
- Money transferring
- Real-time checking mechanism
- Insurance management
- Asset management
- Stock exchange and cryptocurrency exchange
The functions mentioned above a just a few of many functions there are that you should have in a fintech app. Based on what niche market you are targeting, you can sort out what functions are the most important ones and put them on your fintech applications.
Data analytics
Data analytics is another important feature that you can’t miss when building a fintech app. Users now want to see every little detail and hourly report on their spending and financial activities. Of course, they would look for an application that can provide them with the data they need.
For the customers, when the app puts the tracking of users’ financial activities, the customers can now view their transaction history, set goals for saving money, track what they have done with the funds and generate reports. This is a plus point that anyone would highly appreciate.
For the business’ side, Fintech companies will have the chance to analyze data and get some insights to offer better financial advice to their clients. From their spending and the data on their savings, they can now devise loan schemes or personalized services for their clients.
Notifications and Updates
The notifications are among the first features to implement for fintech applications as this is the direct line of communication between users and the application. For fintech apps, you need to develop real-time notifications to keep your users stay-up-to date to any announcement. For example, any news on the bills, fraudulent alerts, spending, payments, etc. are the ones that need to be notified immediately if there are any.
It is the natural preference for people to want to stay updated. They want to get access to the most frequent technologies. When an application doesn’t have the trending features, many users are likely to switch to another one with better and newer features.
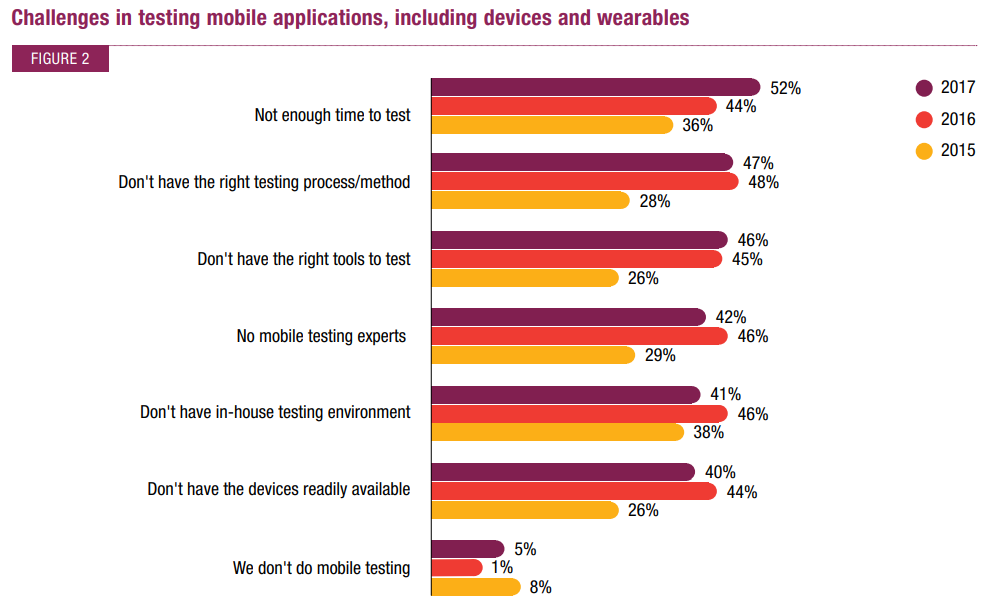
According to a survey conducted by PwC, 68% of the correspondents want to stay up-to-date with the latest technologies, although many of them find it hard to use them.
Payment gateway
Although payment is part of the basic functions of finance, it is an important one as it is present everywhere in our daily lives. The pace of life is getting faster and faster, and people want to do things as fast as possible, leading to the urgent demands for easy payments. This means that you should always include scanning and QR codes in your fintech app.
Plus, you should also concentrate on integrations within multiple fintech apps to extend the functionality and meet numerous users’ demands. This also adds enhanced functional capacity to your fintech app.
E.g. Banking app that connects to virtual wallets, making payments easier.
RPA in chatbots and other virtual assistant services
Robotic Process Automation utilizes digital robots to automate daily routine tasks. It has been adopted and implemented by many businesses in the world.
In a small survey of Deloitte Global RPA Survey, 53% of respondents have already started their RPA journey and further 19% of respondents plan to adopt RPA in the next two years.
This new technology is promised to cut down some operational costs massively as it can help us in:
- Automation in data validation & data migration between banking applications
- Customer account management
- Report creation
- Form filling
- Loan claim processing service
- Loan data updates
- Back-up of interest teller receipt
RPA can also handle a high volume of data at the same time without a glitch, which will be of great advantage to the customer experience. For advanced RPA, they can have the learning capability to take the customer experience to the next level.
2. The technical requirements to build a fintech app
In software projects, technical requirements typically refer to how the software is built, for example: which language it’s programmed in, which operating system it’s created for, and which standards it must meet.
To develop a fintech app successfully, choosing the right technologies is crucial. The tech stack selected affects the scalability, maintainability of the app, development time, and costs.
Below we consider three common app development approaches and relevant technologies to create a fintech app:
- Mobile app development
- Web app development
- Hybrid development
Mobile app development
As mobile penetration is ubiquitous among us, the concept “mobile-first” is the most common thing you might encounter when starting the process of fintech app development. The term “mobile-first” shows how important it is for mobile app development to be carried out.
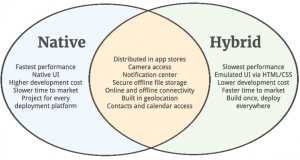
While native app development is suitable for building a fintech application that will run on a specific platform (iOS or Android). This approach involves using specific technologies and tools for a particular platform. You can take a look at the tools and technologies for mobile app development here.
Web app development
Web app development involves creating apps that use remote servers and run on mobile and desktops. This is a great way to be outside of the app stores and be available for both mobile and desktop users.
Hybrid development
Hybrid development can be the optimal solution in some cases that developers want to create an app that is both native and web. The application’s core is created using web technologies wrapped in a native container. Hybrid apps operate like websites but can use features of the mobile device.
There are a great variety of technologies and tools for fintech app development. To make the right choice, it’s necessary to consider such factors as app type, scalability, time to market, and security that are vital for every fintech app.
3. How much does it cost to create a fintech app?
Before going further into how to calculate the fintech app development cost, we should take a look at how much did it cost the giants in the field.
There’s been no confirmation of how much did it cost, but they estimated the cost of cloning these apps, and they go as follows:
- Facebook at $420,000 – $465,000 (at $150/hour)
- Shopee products somewhere between $100,000 and $300,000
- Applications like Uber, or Grab, with the supply and demand sides, around $142,350 – $178,000
- WhatsApp at $173,550 – $222,600
A 2017 survey of 12 leading app developers by Clutch revealed a wide range of $30,000 to $700,000 to develop a mobile app. Based on the average number of hours required to create an iOS-only app, they established the average cost to be $38,000 for a simple and $171,000 for a complex app.
Please be noted that the above applications are the top player both in fintech and the digital market in general, hence the high cost. For application with simpler operations and smaller scopes, the price varies according to the following factors:
- Type of fintech app (investing, banking, insurance, etc.). All of these apps require a high level of cybersecurity. However, with applications related to the stock market or cryptocurrency exchange, real-time fluctuations and need to be updated every second. Especially for the cryptocurrency market with hundreds of coins entering and getting out of the exchange every day, the developer team has to work on the algorithms to provide the most accurate insights of the data. For applications that deal with such new and complicated matters, the fintech app development cost will be higher.
- The number of required features. This can also be understood as the complexity of the app. The more features you want to involve in one single application, the more you have to spend on developing it.
- The platform you’re opting for (iOS, Android): There is a slight difference in the cost of an iOS and an Android application. Normally, to build an iOS app, you would have to spend more than you would with an Android app. The complexity of the app is another factor that defines the cost. A price tag for a simple app with a basic User Interface and a set of must-have features ranges from $40,000 to $60,000, Medium complexity app development project costs between $61,000 and $120,000 and, finally, a Complex app project would require at least $120,000 investment, if not more.
- Mobile app development approach: According to app development companies, the average cost to build a mobile app can be $1, 00,000 – $5, 00,000. On average the hybrid app development cost should be $5000 – $1,000,000, and it would take approximately 200 – 5000 hours to build.
- Needed technologies (languages, libraries, frameworks, Blockchain, AI, VR, etc.). Such technologies as Blockchain or AI/VR are trending, but the number of IT talents that have experience in these fields is not high.
- Team size: The bigger the team size is, the more it can cost you. Remember that the team has to include designers, testers, developers, BA, DevOps, Scrum master, etc. and each one of them can cost a fortune to recruit.
- Cost of deployment and support: App Store and Google Play fees, admin, servers and backend support, customer support, legal, and further development costs. Initial setup and basic controls, data storage, third-party integration, access to enterprise data, data encryption, and scalability. Maintenance expense, Copyright & legal fees, Sales and marketing.
If you cannot afford the management cost of an in-house team, there are other cooperation models that you can try, namely outsourcing company, hiring freelancers, etc.
Looking for a team to take care of your fintech app? Don’t hesitate to contact Lotus QA for quotations. We will help you vest out a reasonable pricing plan.
Contact us:
- Website: https://www.lotus-qa.com/
- Tel: (+84) 24-6660-7474
- Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/LotusQualityAssurance