Black Box Testing: Fundamentals, Techniques, and Guide
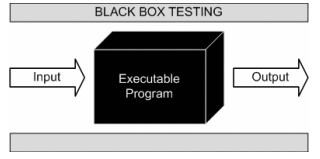
Black box testing is a popular software testing methodology. It mainly focuses on the input and output of software applications and doesn’t care about the internal code structure of the software.
In this blog, LQA will give you a fundamental guide to black box testing, covering its mechanism, types, techniques, process, and differences from white box testing and gray box testing.
Let’s dive in!
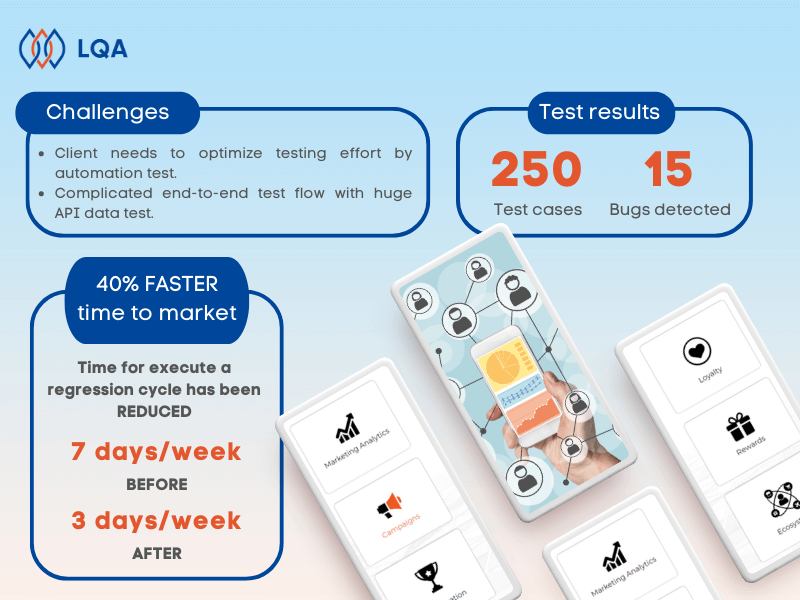
Black Box Testing Fundamentals
What is black box testing?
Black box testing is a software testing methodology in which testers know what the software is supposed to do but don’t know the internal code structure of the software.
Hence, black box test cases are built around specifications and requirements, such as how the application is expected to behave.
Black box testing can be applied to both functional and non-functional testing at every level of software testing: unit, integration, system, and acceptance. Its major objective is to evaluate the software’s functionality, identify errors, and ensure that it meets specified requirements
Example of black box testing
Consider an e-commerce web app. As a black box tester, you check if the app’s login functionality works as expected by entering valid and invalid credentials and verifying the system’s response.
Below is an example of black box test cases to test the login function of the app, in which T = true and F = false.

Example of black box testing
Black box testing tools
Depending on the specific test types, we have different black box testing tools, such as:
- Functional testing: Selenium, JUnit
- Performance testing: Apache JMeter, LoadRunner
- Security testing: OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite
- Usability testing: UserTesting, Crazy Eg
Pros and cons of black box testing
So, what are the advantages and limitations of black box testing?
Pros of black box testing
The advantages of black box testing include simplicity, realistic evaluation, user focus, early bug detection, and unbiased tests. Here are why:
- Simplicity: Black box testing doesn’t require knowledge of internal code, allowing a quick and easy start compared to white box testing and gray box testing.
- Realistic evaluation: Black box testers focus on the output of the software application and how the software works in reality.
- User focus: Black box testers evaluate software functionality as users, from a user perspective, hence increasing the likelihood of user acceptance.
- Early testing: Black box test cases can be designed right after the completion of specifications and executed in the early stages of software development, allowing for early detection of functional issues.
- Unbiased tests: Black box testers provide an unbiased, fresh perspective as they lack knowledge of the internal workings of the app.
Cons of black box testing
Black box testing also has some drawbacks, such as:
- Dependence on documentation: Black box testing test case design relies heavily on accurate and comprehensive specifications, which may not always be available or up-to-date.
- Limited code coverage: Black box testing may miss certain code paths and internal logic, reducing the depth of testing coverage.
- Inefficiency for complex systems: It may not effectively pinpoint intricate code-related issues in complex software architectures, due to its inability to directly access and analyze the internal code structure.
- Potential for redundancy: Tests can be redundant if already run by the software designer and developers.
Types of Black Box Testing
Black box testing is applied to 3 major test types: functional testing, non-functional testing, and regression testing.
Functional testing
Functional testing ensures that the software functions as intended. It tests features like input validation, user interface, and data manipulation.
Some common types of functional testing include smoke testing, sanity testing, integration testing, system testing, and regression testing.
Black box testing in functional testing involves creating test cases based on external specifications, executing them to validate functionality, and ensuring that the software meets specified requirements without knowing the internal code.
Non-functional testing
Non-functional testing focuses on aspects other than functionality, including performance, security, usability, and reliability.
In other words, while functional testing checks if the software performs a specific action, non-functional testing checks how the software performs that action under different conditions.
In non-functional testing, black box tests can assess whether the software:
- is user-friendly
- performs well under various loads
- is compatible with different browsers, devices, and environments
- remains secure against common threats and vulnerabilities
Regression testing
Testers can use black box testing techniques in regression tests to verify whether new changes affect the existing functioning of the system.
Regression testing is often done when there are modifications to a system, such as developing a new function, fixing a bug, or maintenance. In apps with frequent updates, regression testing is often automated for optimal efficiency.
Also read: Software testing basics, principles, skills, phase
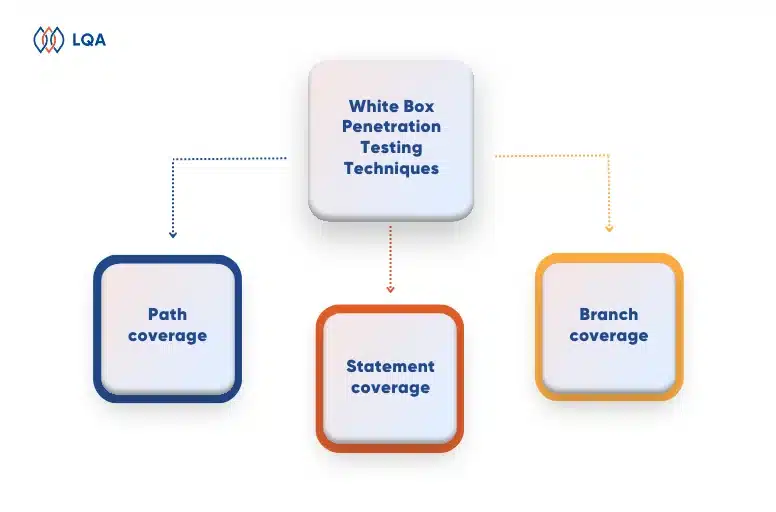
Black Box Testing Techniques
There are many black box testing techniques that apply to different logics within software applications. Here are the 5 major techniques.
| Black box testing technique | Description |
| Boundary value analysis (BVA) | Test the boundaries between partitions. |
| Equivalence class partitioning | Divide the input domains into equivalent classes and test one input from each class. |
| Decision table based testing | Used when the output responds to varied combinations of input. |
| State transition testing | Verify system behavior during state changes. |
| Error guessing | Use testers’ intuition and experience to “guess” errors. |
All the above black box testing methods can be done without knowing the internal workings of the system, hence are called black box testing. Let’s dig into them!
1. Boundary value analysis (BVA)
Boundary value analysis, short for BVA, is a black-box testing technique to test the boundaries between partitions instead of testing multiple values in the equivalence region. In BVA, testers assume that if it is true for boundary values, it is true for the whole equivalence region.
Example of BVA:
Let’s say you’re testing a system where valid age values are between 20 and 50.
- Test with the minimum boundary value (20). It should be valid.
- Test with the maximum boundary value (50). It should be valid.
- Test just below the lower boundary (19). It should be invalid.
- Test just above the upper boundary (51). It should be invalid.
2. Equivalence class partitioning
In equivalence class partitioning, also known as equivalent partitioning, testers divide all possible inputs into various equivalence data classes (or data groups) and test only one example input from each class, assuming that data in each class behaves the same.
Example of equivalent partitioning:
Imagine you’re testing a system where valid usernames are within 5 – 20 text-only characters. You divide the inputs into 5 groups as below.
| Valid input group | Example input | Invalid input group | Example input |
| Inputs between 5-20 text characters | 10 text characters | Inputs below 5 characters | 3 text characters |
| Inputs above 20 characters | 25 text characters | ||
| Empty input | (Leave blank) | ||
| Inputs contain non-text characters | 10 characters contain text and numbers |
Then, you pick one representative input from each group to test. For instance, if you input 10 text characters, it should be valid. But if you input 4 characters, it should be invalid.
3. Decision table based testing
Decision table, also called a cause-effect table, is a software testing technique based on cause-effect relationships. It is used to test system behavior in which the output depends on a combination of inputs, for instance:
- Combination of inputs: all blanks/specific blanks in the log-in section are filled in by a user.
- System behavior: navigate the user to the homepage.
Example of decision table testing:
An app allows users to log in only when the username, password, and captcha are correct. We have the below table that represents all possible scenarios to test, in which T = true and F = false.

Example of decision table testing
4. State transition testing
In state transition black-box testing, changes in the input make changes to the state of the system and trigger different outputs. In this technique, testers execute valid and invalid cases belonging to a sequence of events to evaluate the system’s behavior.
Example of state transition testing:
An e-commerce app will lock a user’s account if he/she enters the wrong password 3 times in a row. This means the user will be able to log in if he/she enters the correct password on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd try. Each time the password is entered correctly, the state is transitioned into “Access accepted”. Otherwise, the state turns into “Account locked” after the 3rd time entering the wrong password.
The state transition diagram below represents a sequence of events to test.

5. Error guessing
In error guessing, you rely on testers’ intuition and experience to anticipate and uncover possible errors or error-prone situations in the software, particularly in situations where formal test cases may be insufficient.
In error guessing, the test cases could be based on:
- Previous experience in testing related/similar software products.
- Understanding of the system to be tested.
- Knowledge of common errors in such applications.
- Prioritized functions in the requirement specification documents (to not miss them).
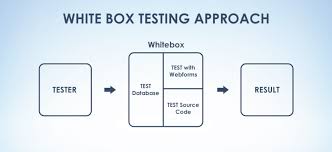
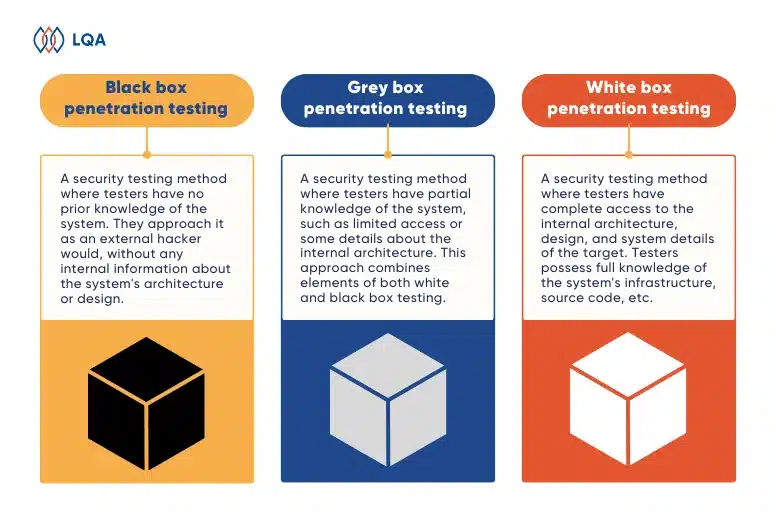
Black Box vs. White Box vs. Gray Box Testing
Black box, white box, and grey box testing make up the three software testing methodologies to test an app as an outsider, an insider, and a partial insider. While black box testing and white box testing are opposite concepts, gray box testing stands in between the two.

Black Box vs. White Box vs. Gray Box Testing
Let’s dive into a detailed comparison between black box, white box and gray box testing.
| Black box testing | Gray box testing | White box testing |
| Minimal to no knowledge of internal details | Partial knowledge of internal details | Full knowledge of internal details |
| Low-level granularity | Medium-level granularity | High-level granularity |
| Focuses on testing the functionality of the software | Uncover defects, vulnerabilities, and ensure proper functioning of the software | Test the internal logic, code structure, and implementation details of the software |
| Evaluates a product from the user’s perspective | Considers both the user’s perspective and developer’s perspective | Evaluation happens from the developer’s perspective |
| Is often done by end-users, testers and also developers | Can be done by developers, testers, and end-users | Is generally done by developers and testers |
| Test cases are designed on the functional specifications | Test cases are created based on both functional specifications and some internal knowledge | Test cases are designed based on the internal code and structure |
| Tend to consume the least time among the 3 methods | Tend to consume medium time among the 3 methods | Tend to consume the most time among the 3 methods |
Technique:
|
Technique:
|
Technique:
|
How To Perform Black Box Testing?
A standard black box testing process takes place as below:
- Examine the requirements and specifications of the software
- Define the testing scope, objectives, and create a test plan
- Develop test cases based on specifications and user scenarios, including choosing valid inputs, invalid inputs, and expected output for each input.
- Execute the test cases, entering inputs, observing outputs, and comparing real outputs with expected outputs.
- Document any discrepancies or defects found during testing.
- Re-run tests after fixes or changes to ensure existing functionality remains intact.
Frequently Asked Questions about Black Box Testing
1. What are the types of black box testing?
Black box testing is suitable for three primary types of tests: functional testing, non-functional testing, and regression testing.
2. Is black box testing illegal?
No, black box testing is not illegal. It is a legitimate and widely used software testing method where testers assess the functionality of a system without knowing its internal code.
However, it’s crucial to conduct black box testing on systems you have permission to test, respecting ethical and legal boundaries. Unauthorized testing on systems or networks without proper consent is considered illegal and can result in legal consequences.
3. Why might companies prefer black box testing over white box testing?
Black box testing is user-focused and doesn’t require knowledge of internal code. Hence, it is often simpler to start and more cost-effective to carry out compared to white box testing and gray box testing. That’s why companies may prefer black-box testing over white-box testing.
Black Box Testing with LQA
As the pioneering independent software testing company in Vietnam, Lotus Quality Assurance (LQA) stands out as a prominent software quality assurance firm with a wide range of software testing services, covering black box, gray box, and white box testing.
Are you looking for experts in conducting black box testing services? Don’t hesitate to contact LQA’s software testing team.
Related resources:



















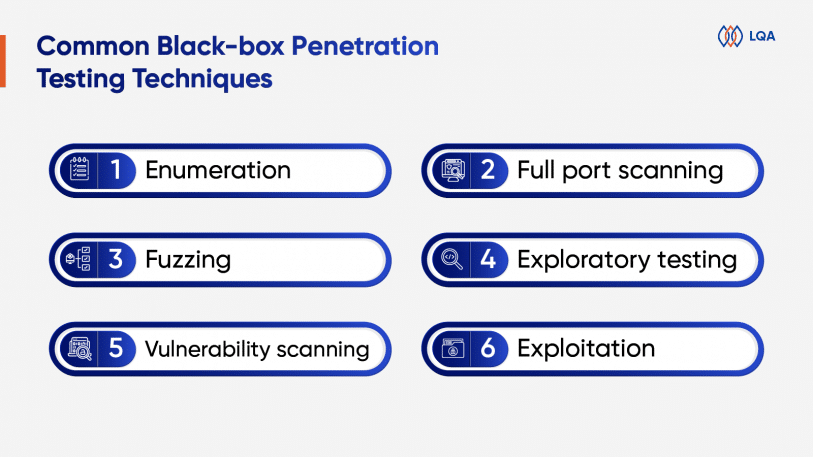 Enumeration
Enumeration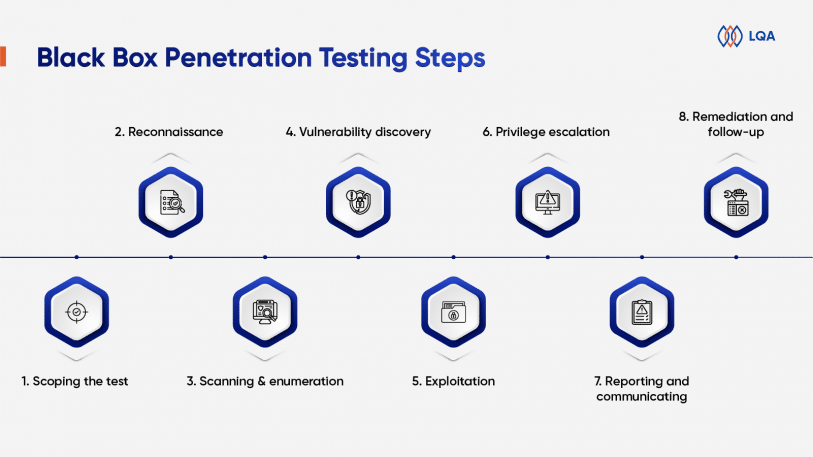 1. Scoping the test
1. Scoping the test