An Ultimate Guide to Offshore Software Testing Success
The trend of outsourcing software testing, particularly to offshore companies, has gained momentum in recent years and it’s for good reason – substantial cost savings.
Indeed, a 2023 study by Zippia revealed that 59% of respondents view outsourcing as a cost-effective solution. This advantage is largely attributed to the lower labor costs found in notable offshore software testing centers like Vietnam. Notably, according to the same research, U.S. businesses can achieve labor cost reductions ranging from 70% to 90% by overseas outsourcing.
Keep on reading to learn about the structure of an offshore software testing team, important considerations for effective outsourcing, strategies for maximizing the benefits of this model, and much more.
What is Offshore Software Testing?
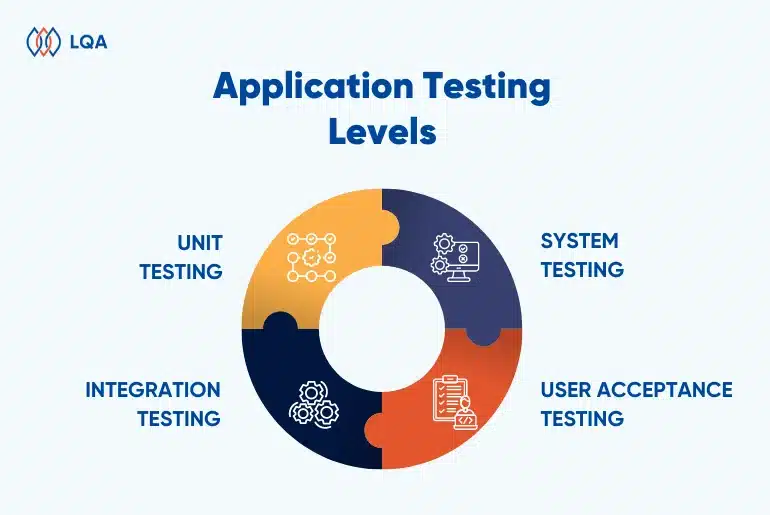
Offshore software testing refers to delegating the software testing process to a service provider located in another country, often in a different time zone. Rather than maintaining an internal team for these tasks, companies collaborate with offshore partners to execute various testing types such as application testing, mobile testing, agile testing, functional testing, and non-functional testing.
Also read: 6 reasons to choose software testing outsourcing

What is Offshore Software Testing?
Onshore vs. offshore software testing
To better understand offshore quality assurance (QA) testing services, it’s important to clarify that geography plays a significant role in this definition. This means that not all remote teams qualify as offshore and if they’re based in the client’s country, sharing the same working hours and language, they’re still classified as onshore testers.
For your quick reference, check out the comparison table below:
|
Aspect |
Onshore software testing | Offshore software testing |
|
Location |
Conducted within the same country | Executed in different countries |
|
Time zones |
Same time zone | Different time zones |
|
Cost |
Higher due to local labor expenses | More cost-effective thanks to significantly lower labor costs in potential outsourcing countries like Vietnam |
|
Communication |
Facilitates smoother and more consistent communication between teams, reducing misunderstandings from language barriers | May experience miscommunication resulting from language differences |
|
Association |
Allows for easier management of testing requirements and greater control over personnel | Requires strong coordination and thorough project management |
|
Proficiency and quality |
Benefits from local expertise and quality | Gets access to a diverse talent pool with varying levels of quality |
|
Legal and compliance |
Aligns with local regulations | Must adhere to global legal and compliance standards |
Learn more: A complete comparison of nearshore vs. offshore software outsourcing
Structure and Responsibilities of the Perfect Offshore Software Testing Team
The offshore testing team’s structure and size are shaped by different factors, such as the project’s complexity, timeline, and existing resources. However, a typical structure includes 7 key roles as outlined below.
It’s worth noting that not every company requires all of these roles; therefore, businesses should tailor their team composition based on their unique needs.

Structure of the Perfect Offshore Software Testing Team
Manual QA testers
Manual testers are the backbone of most testing projects, handling a large portion of the workload. For mid-sized projects, a team of 3-5 manual QAs is generally sufficient.
QA lead
The QA lead manages the manual QA team, fostering effective communication and coordination. In some instances, this role may be filled by a senior member of the team, who also engages in hands-on testing activities while leading the group.
Automation QA specialists
Automation testers are indispensable for mid- to large-scale projects, particularly those that involve repetitive tests, such as regression testing. Automation specialists typically join the project after manual testers have made initial progress. In some cases, they may start earlier if preliminary tests have been completed by a prior team.
Automation QA lead
The automation QA lead supervises the automation QA team and also participates in numerous testing tasks. Often, the automation lead joins the project before the rest of the team to set up a strong foundation for subsequent work by the automation QAs.
Project manager (PM)
This key role acts as a liaison between the client and the vendor. While a PM can work on the vendor’s side, this arrangement is most suitable for larger projects that deliver services beyond testing. For most testing projects, having a PM on the client’s side is preferable.
DevOps engineer
Responsible for creating the necessary infrastructure, the DevOps engineer makes sure that both development and testing teams have everything they need to operate effectively without interruptions. While a DevOps engineer can work on the client’s side, having a dedicated DevOps engineer within the vendor’s organization often provides more advantages.
Business analyst (BA)
The business analyst gathers business data and insights to recommend pathways for organizational success. The involvement of a BA in a testing project—at least on a part-time basis—can significantly enhance the quality and outcome of the software produced.
In addition to these 7 roles in a testing team, the presence of a development team also greatly contributes to the success of a QA project. This is because without developers available to address bugs identified during testing, the offshore testing team may find itself limited to conducting only initial tests, leading to potential delays in the overall process. Many organizations benefit from harnessing two offshore teams—one for development and another for testing—or maintaining an in-house development team.
Also read:
- Offshore software development comprehensive guide for 2024
- Essential guide for offshore development center setup
- Offshore software development rates by country
- Top offshore software development company review in 2024
Key Considerations When Hiring an Offshore QA Testing Team
Whether a company requires a team for a short-term project or is looking to establish a long-term partnership, selecting the right offshore software testing company is a critical decision. Hiring offshore software testing teams without a well-thought-out process can lead to unsatisfactory outcomes.
To achieve successful and mutually beneficial QA collaboration, organizations should take into account 4 key factors as follows:

Key Considerations When Hiring an Offshore QA Testing Team
Expertise and experience
Evaluating the provider’s experience within a specific industry and with projects of similar scale holds significant importance. A partner with a background in the same sector or comparable projects is more likely to deliver results that align closely with future business requirements.
Besides, look for a team with a strong track record in testing methodologies and tools relevant to the project needs. Checking the offshore team’s proficiency with the latest QA technologies and methodologies also helps confirm the project benefits from advanced testing practices.
Additionally, versatility in testing approaches enhances the ability to adapt to differing project needs.
Communication and collaboration
Having clear and consistent communication forms the foundation of any successful partnership. Therefore, companies should prioritize offshore partners that demonstrate strong communication skills and use tools that seamlessly integrate with existing collaboration platforms like Slack and Microsoft Teams.
Security and compliance
Conducting a careful review of the vendor’s security protocols and their compliance with relevant data protection regulations is a must for safeguarding sensitive project data. One useful approach to gauge their handling of these matters is to reach out to the provider’s previous clients for insights.
Cost and pricing model
Rather than settling on the first option, businesses should explore various pricing models from multiple providers since it’s of great importance to opt for the offshore testing team whose pricing structure fits the organization’s budget and project needs.
For more tips on optimizing software testing costs, feel free to check out our blog about how much does software testing cost and how to optimize it.
Learn more:
- Top 10 software testing companies in Vietnam 2024
- Top 10 software testing companies in the world in 2024
How to Make the Most of the Offshore Software Testing Team?
Choosing the right vendor and building a well-structured team are just the first steps. Continuous and efficient management of offshore testing partners is equally vital in maintaining the QA project’s desired quality.
Here are 5 key strategies to better manage offshore QA testing teams:
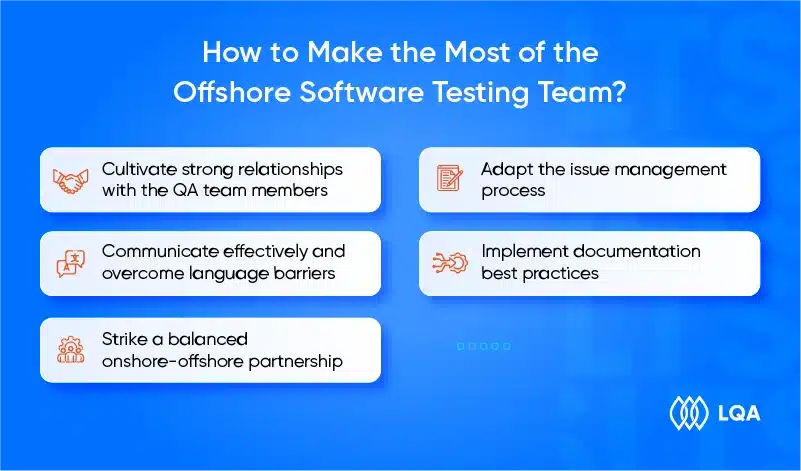
How to Make the Most of the Offshore Software Testing Team?
Cultivate strong relationships with the QA team members
A strong rapport and a foundation of trust with the offshore testing team profoundly influence the project’s success.
Begin by building personal connections with them, learning their names, pronunciations, etc.
Encourage team members to create simple slides introducing themselves, including photos and basic information. This is especially helpful when integrating in-house and offshore QA teams.
A project manager might be just the right person to facilitate these connections and strengthen team dynamics.
Communicate effectively and overcome language barriers
Most offshore QA team members possess a good command of English, sufficient for handling technical documentation and day-to-day interactions.
Nevertheless, communication challenges might still arise, especially in offshore settings.
Regular team meetings, structured communication protocols, open discussions, and informal check-ins are a few ways to alleviate potential misunderstandings.
Strike a balanced onshore-offshore partnership
It’s not advisable to assign all testing tasks to offshore teams solely to reduce costs.
Instead, organizations should evaluate which testing activities can realistically be managed by offshore experts, taking into account the complexity of business processes and any access challenges related to testing systems.
This approach clarifies roles and responsibilities for both in-house and offshore teams, allowing for appropriate task assignments based on each team member’s strengths and expertise.
Adapt the issue management process
Using management tools for documenting and tracking defects is common practice, but many projects overlook the importance of effective issue management to address functional, technical, and business-related questions that an offshore quality assurance team may encounter during testing.
To optimize this process, companies should encourage the offshore testing team to utilize a robust web-based document management system.
In addition, don’t forget to leverage time zone differences since a significant time gap can be transformed into an opportunity for near-continuous testing operations and maximizing productivity.
Implement documentation best practices
Another helpful tip is maintaining proactive, clear, and thorough documentation. Starting this process early—even before project launch—enables all stakeholders to quickly access relevant materials to preempt or resolve possible misunderstandings.
Organizations should establish firm guidelines that encompass all areas of documentation: test scenarios, test scripts, execution procedures, results documentation, etc.
Choosing a suitable test management tool is based on the company’s specific needs, but accessibility across locations and proven effectiveness should top the list of criteria.
How Does Offshore Software Testing Operate At LQA?
LQA offers a host of offshore software testing services, ranging from software/hardware integration and mobile application testing to automation, web application, and embedded software testing.
We pride ourselves on providing access to top-tier Vietnamese QA engineers. Our commitment to quality is evident in our impressive track record: a leakage rate of just 0.02% and an average CSS point of 9/10.
Central to LQA’s success is a clearly defined workflow that enables our testing experts to approach each project systematically and efficiently.
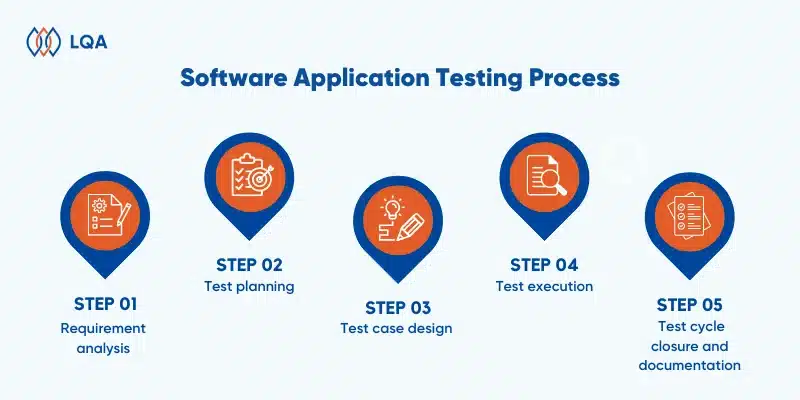
Here’s a step-by-step look at our process:

How Does Offshore Software Testing Operate At LQA?
Step 1. Requirement analysis
Our skilled testing professionals start by gathering and analyzing the client’s requirements. This critical step allows us to customize the software testing lifecycle for maximum efficiency and formulate pragmatic approaches tailored to each project.
Step 2. Test planning
Once the LQA team completes the requirement analysis and planning phase, we clearly define the test plan strategy. This involves outlining resource allocation, test environment specifications, any anticipated limitations, and a detailed testing schedule.
Step 3. Test case development
Guided by the established test plan, our IT experts create, verify, and refine test cases and scripts, ensuring alignment with the project objectives.
Step 4. Test environment setup
LQA’s team meticulously determines the optimal software and hardware conditions for testing the IT product. If the development team has already defined the test environment, our testers perform a thorough readiness check or smoke testing to validate its suitability.
Step 5. Test execution
With over 8 years of experience in quality assurance, our dedicated testers execute and maintain test scripts, carefully documenting any identified bugs to guarantee the highest quality.
Step 6. Test cycle closure
After finishing the testing process, our offshore software QA team generates detailed reports, conducts open discussions on test completion metrics and outcomes, and identifies any potential bottlenecks to streamline subsequent test cycles.
Pros and Cons of Offshore Software Testing

Pros and Cons of Offshore Software Testing
Pros
- Cost-effectiveness: Lower labor costs in many offshore locations translate to significant budget savings.
- Expanded talent pool: Organizations gain access to a global network of skilled testers with specialized offshore QA expertise.
- Scalability and flexibility: Offshore teams can be adjusted quickly to accommodate evolving project needs, offering both short and long-term engagement options.
- 24/7 testing coverage: Continuous testing support and faster iteration cycles are possible with round-the-clock operations.
- Government support: Governments in many regions, including Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe, incentivize offshore partnerships with favorable tax incentives and legal frameworks.
- Comprehensive documentation: Offshore testing services providers often adhere to rigorous documentation standards, providing transparency and reducing miscommunication risks.
Cons
- Communication barriers: Language and cultural differences require proactive management to mitigate misunderstandings.
- Time zone differences: Clear communication and potentially staggered schedules are necessary to bridge time gaps.
- Intellectual property protection: Thorough due diligence and robust security measures are crucial when entrusting sensitive information to offshore software testing companies.
Future Trends in Offshore Software Testing
Software testing offshore is changing rapidly to keep pace with technological advancements and industry demands. While predicting the future with absolute certainty is impossible, several trends are likely to shape the industry moving forward.

Future Trends in Offshore Software Testing
- Artificial intelligence & machine learning integration: Artificial intelligence and machine learning are expected to drive smarter automation, from test case creation and defect prediction to self-healing tests.
- DevOps & agile integration: The integration of development and testing teams is becoming increasingly important for expediting release cycles and improving overall product quality. Offshore teams are poised to play a crucial role in continuous testing and feedback loops, carrying out a seamless development process that adapts to shifting requirements.
- Blockchain in offshore software QA: Blockchain technology introduces secure, tamper-proof solutions for managing testing artifacts and data. By delivering trust and transparency in the testing process, blockchain can improve the integrity of testing operations, making it an attractive option for organizations seeking reliable and verifiable testing outcomes.
FAQs about Offshore Software Testing
What is offshore software testing?
Offshore software testing refers to delegating the software testing process to a service provider located in another country, often in a different time zone. Rather than maintaining an internal team for these tasks, companies collaborate with offshore partners to execute various testing functions.
When should I consider using offshore software testing?
Offshore software testing proves advantageous in many scenarios:
- Large, complex, or long-term projects: When testing demands exceed internal resources.
- Budget or time constraints: Accessing potentially lower labor costs and 24/7 testing coverage.
- Focus on core competencies: Freeing up internal teams by delegating specialized testing.
- Global market expansion: Leveraging expertise in testing for different languages and regions.
- Access to cutting-edge trends: Tapping into providers at the forefront of testing innovations.
How do I choose the right offshore testing provider?
To choose the right offshore testing partner, conduct in-depth research and consider these essential factors:
- Reputation & experience: Look for established providers with a proven track record and positive client testimonials.
- Expertise & skills: Ensure the provider possesses the required technical skills and domain knowledge relevant to your project.
- Quality assurance: Inquire about quality control measures, certifications, and adherence to industry best practices.
- Tools & infrastructure: Verify access to the necessary testing tools, environments, and infrastructure.
- Communication & culture: Prioritize clear communication, cultural fit, and a collaborative approach.
What are the key considerations for effective offshore software testing?
Successful offshore software testing depends on numerous factors.
- Crystal-clear communication: Define project requirements, expectations, and timelines upfront.
- Seamless collaboration: Maintain regular communication and leverage collaborative tools for progress monitoring.
- Timely feedback loops: Establish a system for providing prompt and constructive feedback on testing results.
- Strong partnership: Cultivate a relationship built on transparency, trust, and mutual understanding.
Final Thoughts about Offshore Software Testing
Engaging in offshore software testing brings numerous advantages for organizations. However, selecting the right team necessitates careful consideration of different factors, from expertise, communication, and security measures, to pricing structures.
By establishing a well-structured offshore software testing team and implementing the right strategies and best practices, firms can harness this approach to achieve superior software quality, quicker time-to-market, and greater cost efficiency.
For those seeking trustworthy, professional, and experienced offshore software testing services, LQA stands out as a top provider. With over 8 years of experience, we deliver high-quality and cost-effective software testing solutions to clients worldwide. Our offerings include quality assurance consulting and software testing implementation across a wide range of software testing services, such as software/hardware integration testing, mobile application testing, automation testing, web application testing, and embedded software testing.
- Website: https://www.lotus-qa.com/
- Tel: (+84) 24-6660-7474
- Mail: [email protected]
- Fanpage: https://www.linkedin.com/company/lqa/
























 Increased Use of AI and ML
Increased Use of AI and ML