Software development models
Software development models
Software testing is an integral activity of software development activities. If the software development process is the backbone that creates the basic software programs, then the testing process will cover the muscles in accordance with customer requirements to help complete a qualified figure. Knowing the soft development model will help you have a view of orienting and building the right, more effective and appropriate testing activities.
In this article, we will share with you 3 popular software development models that’re widely used in the technology space with their pros and cons.
1. Waterfall – Software models
Waterfall software development methodology is the model when all stages are clearly defined at the beginning, and the development process will strictly follow a pre-defined plan without much flexibility to adjust things.
Stages of development in the Waterfall model:
・Requirements collecting: collect information about product details and features from customers as much as possible.
・Design: plan which programming language (Java or .NET, etc.) you will use, which database (Oracle or MySQL, etc.) as well as the general features and architecture of the product. Products.
・Construction: After design is the construction phase (writing code for the product).
・Test: check if the product is built according to the customer’s original requirements or not.
・Deployment: Deploy products to customers.
・Maintenance: After deploying a product to a customer, you may receive a request from a customer to customize or modify the product.
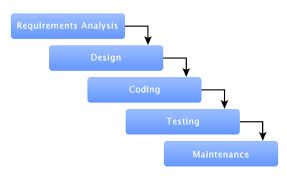
Waterfall software development model
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
The stages are clearly defined inputs and outputs |
Requires all software requirements to be clearly defined at the outset of the project. But most practical projects that require software often contain uncertain issues. |
| Software products are formed through a sequence of clearly sequenced activities. | The actual project is rarely done fully during the project cycle. Besides, the close date of sending a program to customers or being modified directly leads to the software specification not fully reflect what was modified in the source code. |
| There are hidden risks that can only be detected at the final stage and the cost to repair can be very high. |
2. V-model
V-model is a successor to the waterfall software development model yet adding testing phase to each development phase. Corresponding to each stage of the development cycle is the corresponding test phase as the below image. The left side of the V-model is the software development cycle (life cycle). And the right of the V-model is the corresponding test operation.
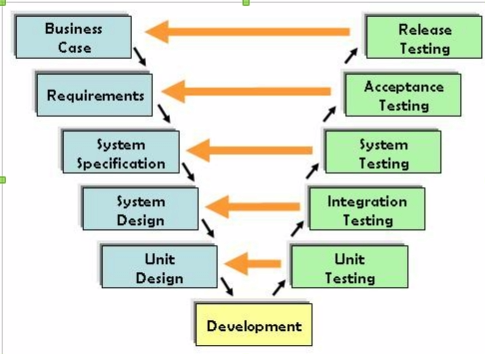
V-model in software development
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Simple, easy to use. | Few flexibility and rigidity exist. It is also shown that every step must have one – test stage, if the project requirements are not too complicated and easy to implement, then performing many such tests is time consuming. |
| There are activities, specific plans for the testing process. | Like the waterfall, the project’s product only appears when all the steps are completed, without the original prototype. |
| Save time, and have a higher chance of success than the waterfall. | If there is a technical change in the middle, it will have to go back to the first step, redo, update the document. |
| Testing activities are focused and carried out in parallel with activities related to the required specification and design. Be proactive in bug detection, find bugs right from the start. |
3. Agile – Software models
Agile is the “iterative” development model. In this type of model, software development is carried out in stages and each stage only focuses on developing one or several product features. In addition, each project is divided into several small areas for ease of use and change when customers request changes. Every small part of the project will be tested right during the project. It is required to meet regularly because in Agile at each time the team must focus on developing an area of the project.
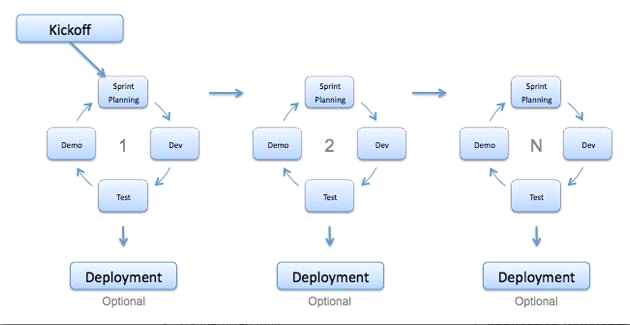
Agile software development model
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
| Agile is a great choice for small projects because small projects often have unspecified requirements and can change often. | Lack of emphasis on design and required documentation |
| With Agile, customers can preview each part of the project during the development process. Because Agile develops software in an incremental way, which can give customers a preview of each completed part. | The size of human resources is usually limited to 7 to 10 people, and it will be a big problem if the required human resources exceed this figure, for example during the exchange meetings. |
For more information about Testing services, please contact us
———————————————————–
Lotus Quality Assurance (LQA)
Tel: (+84) 24-6660-7474
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.lotus-qa.com/
Youtube: Lotus QA channel