Software Testing has always been an indispensable part of a Software Development Life Cycle. While other processes of strategic analysis and software development help build up the “spine” of the whole product with basic functions and interface, software testing is for a well-rounded, fully-functioning product. Get to know the software testing basics in this article now.
Testing is often referred to as test implementation, which means running software and testing. Test implementation includes the process of executing a program or application such as designing tests or checking results, writing test reports, etc.
Check out our testing foundation video series
The Purposes Of Software Testing
The main purposes of the Test include the follows:
- Detect bugs
- Prevent the creation of errors in the system
- Check if the product quality meets requirements
- Provide information to support product decisions, such as if it’s market-ready or not
We need to distinguish the difference between Test and Debug. Test is to find errors, and Debug is to find out the cause of the errors and fix them. The responsibility of testing usually lies with testers, and the responsibility of debugging belongs to the developers.
These are the basic steps for the subsequent coverage of testing. How much effort and time to be spent on the testing process depends on the system structure and the complexity of that system.
To start your journey as a tester, either manual or automation, you need to get acquainted with these fundamentals of testing:
- 7 principles of testing
- 15 skills every software tester should master
- The basic test phases
- Psychology of testing
7 principles of software testing basics
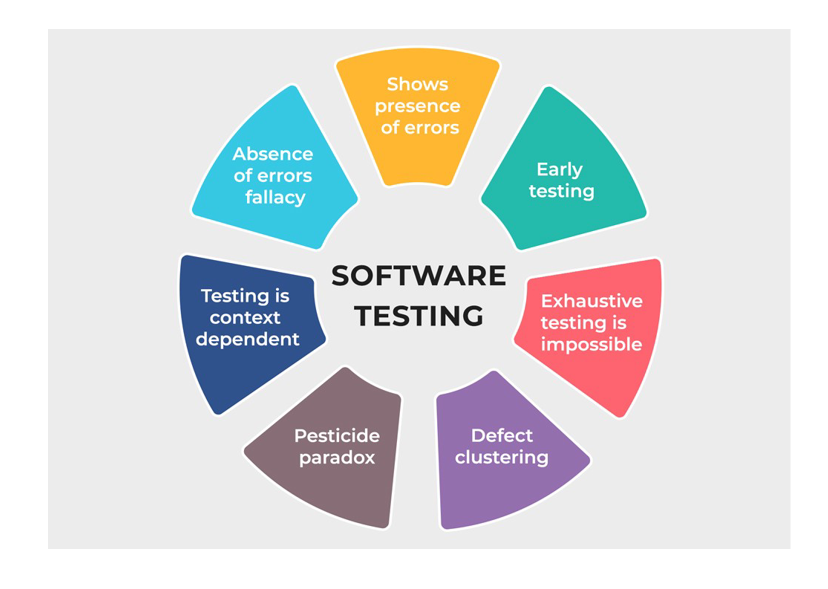
Software Testing Principle – Software Testing basics
Principle 1: Testing can only prove that the software has errors
Software Testing basics – Through testing, we can indicate that the software has errors, but can not prove that the software has no errors at all. Testing can reduce the number of errors in the software, but even in the absence of errors, we cannot claim that our software is error-free.
Principle 2: Testing the entire pattern is impossible
Testing the entire pattern (combining all conditions in data entry) is not possible, except for some extremely simple software. Instead of testing the whole thing, we should rely on risks or priority to focus on the points needed.
Principle 3: Test as soon as possible
To find bugs early, testing should start as soon as possible in the software development process. Different software system requires a different approach for an effective testing process. Test engineers can choose among the popular models, including V-model, Agile, Scrum, etc.
Principle 4: The uneven distribution of errors
It is likely that most errors detected before releasing or during operation are concentrated in certain modules.
Principle 5: The principle of pesticides
When you perform the same test case multiple times, it will eventually fail to find the errors. To avoid this, it is necessary to review and improve test cases periodically.
Principle 6: Testing depends on conditions
For different conditions, there will be different test methods. For example, testing the banking system will be completely different from testing a sales website.
Principle 7: The “bug zero” pitfalls
Do not be so focused on creating a system without errors that you forget the initial requirements from customers. In the end, we are developing a product for certain requirements and purposes, not building bug-free software but no one needs it.
Find the top 10 IT Outsourcing companies for your testing projects
10 Skills every software tester should master
Software Testing basics – Software Testing is evolving at a rapid pace with higher demand over the product and service’s quality. To ensure this, many are applying critical testing methodologies such as agile, DevOps, scrum, etc., all of which are part of the accelerated development and continuous deployment.
Listed below are the 10 skills that every tester needs to know. The skills are categorized as technical skills and non-technical skills.
Technical skills
– Testing Methods: Manual Testing & Automation Testing
Manual testing is usually the first door for testers to enter the testing world. This is when a test engineer rely on on pre-defined test cases and test scenarios, then carry out all test steps manually.
In addition to manual testing is automation testing. It deals with testing on a higher level which requires programming and coding skills. In exchange for a large amount of time spent on writing automation testing code, we can have higher accuracy with a lower cost once the automation testing is implemented.

Manual Testing vs. Automation Testing
Still, both manual and automation testing have their own benefits and can co-exist in a specific testing process. During testing phase of one product, we may see this scenario should be manual while others better come with automated solutions.
The most outstanding feature of automation testing is how it can save up a fortune for business that applies it. With the increasing complexities and advances in software nowadays, the burden of testing is placed heavily on manual testers. Not to mention huge workloads, there are to be stress and tedious testing tasks that manual testers have to deal with. Once automation testing steps in the game, you can instantly recognize the faster pace of the product/service’s time to market.
– DevOps & Agile Methodology
The global market constantly needs more than what they’ve already had. To meet these ever-growing demands, strategists have to put more features, more applications available to the public. This pressing demand to meet delivery deadlines requires collaborative and iterative working models, which should be found in DevOps and Agile methodology.
When you apply Agile methodology, continuous integration and continuous delivery are pushed in an endless cycle of testing, which will eventually speed up the test project.
Software Testing basics – If you combine this methodology with DevOps, you can create cross-functional teamwork right from the development, analysis, and QA. This yields a high-quality product with a faster time to market.
– SDLC
SDLC stands for Software Development Life Cycle. Normally, you can find useful information on how software is made and what steps of it involve software testing. Once you’re familiar with the in-depth knowledge of SDLC, you can anticipate complexities in the application to handle and predict the right testing measures to be done.
– CI/CD
A mature CI/CD DevOps practice has the option of implementing continuous deployment where application changes run through the CI/CD pipeline and passing builds are deployed directly to production environments. Teams practicing continuous delivery elect to deploy to production on a daily or even hourly schedule, though continuous delivery isn’t always optimal for every business application.
– Testing Tools & Techniques
Testing techniques stand as the most practical requirement for test engineers to master. The most common testing techniques needed in the testing process of every product are black-box testing, penetration testing, regression testing, smoke testing. With these testing techniques in hand, testers become more versatile and can handle every task there is.

Automation testing tool is also an important feature for a more cost-effective and high-quality work of testing. With a large number of tools available in the market such as test management tools, GUI testing tools, automation tools, etc., testers can find the suitable ones that can serve different requirements and test purposes in projects with different levels of complexity.
Non-technical skills
– Critical thinking
Although testing is infamous for being tedious and repetitive, once you’re part of the process, you will see that testing also requires a high level of logical thinking and strategic analysis. With these skills, test engineers can identify errors and understand product structure more easily, hence the suitable testing approach and test method.
With a skeptical and multifaceted assessment, testers can validate applications in different usage and scenarios, hence having a practical approach to test their elements dynamically.
– Communication skills
Communication in testing is as important as it is in other fields of the IT industry. These communication skills can help testers deliver their work process and project status to the stakeholders effectively.
An effective approach for communication in a testing project should also include how test engineers inform project requirements, collaborate among team members, etc. Achieving these skills will help in demonstrating a high level of competency on a managerial level.
– Test planning
Test planning skill is essential for any test engineers that want to climb the career path in testing. This skill helps you identify the right approach and appropriate steps to take in testing. Besides all that, test planning also helps in reporting and logging work, giving the stakeholders the overall picture of how the test project is done. To do this, many test engineers devise a well-documented report of the test process and record of what has been done throughout the work.
– Project Management
Consider the test career path with test manager stands at the higher ground, project management skill is a must for any tester want to continue on their career. With this skill mastered, test engineers can answer to stakeholders and be responsible for their team’s work. This also helps them in team management and team assessment.
– Reporting
A good tester must also possess good reporting skills to provide the exact status of the test project and application under test to stakeholders. This practice of reporting leads to better coordination of the overall test project and also gives transparency to the top management in terms of test cases executed, bug encountered, release timelines, etc. which eventually helps in taking the right decisions.
The basic test phases – Software testing basics
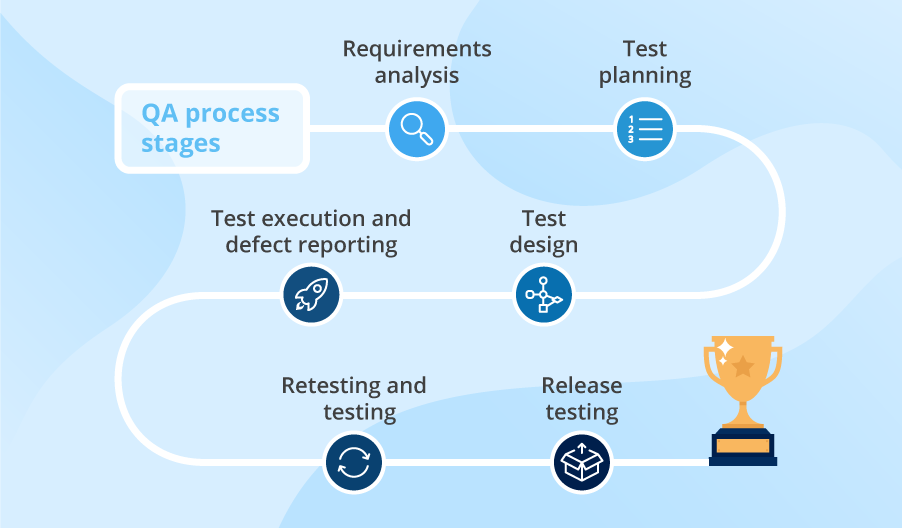
Software Testing Basics – Software Testing Phases
1. Planning and control
Software Testing basics – Test planning is the determination of the purpose of the test and the spec decision. Test control is the activity of comparing the plan with the progress during the test.
Overall, test planning is to identify the objectives of testing and what activities in order to meet these objectives. The main task of planning is to determine the test strategy or approach. Test planning should also clarify scope, risks, required test resources, test schedule, etc. Meanwhile, test Control is the ongoing activity to make sure everything is on track.
2. Test analysis and design
Convert abstract goals into specific test conditions or test designs. Specific example:
- Review for test base such as risk analysis report, interface spec, etc.
- Design test cases with their priority
- Classify the necessary test data
3. Test implement and Test execution
At this stage we will create scripts or test sequences based on test cases and other necessary information, then set up the environment and execute testing.
4. Output and report evaluation
The output evaluation is the evaluation of whether the test implementation is satisfied with the purpose of the Test. For example:
- Compare Test results with specified Test end criteria at the Test Planning stage
- Judge whether you need additional tests or need to change the criteria for the output
- Write Test reports
Psychology of testing

The Psychology of Testing – Software testing principles – Software Testing Basics
Software Testing basics – Testers and Developers always have the same goal – to create a flawless solution for their client’s needs. But they work and think differently. If the developers have a suitable opinion then they can test it themselves. However, separating the environment for the developers and testers will be more effective, and testing from a completely independent standpoint from development by well-trained testers will be more beneficial.
Tester is a reliable and objective third side that can see the possible mistakes and errors that Developer hasn’t predicted. While testing is a constructive job but it is sometimes considered negative so creating a good relationship between testers and developers is extremely important.
To build a good relationship between testers and developers, the following things are needed.
- There is a common goal of creating a good quality product, starting work with a cooperative attitude, not opposition.
- The opinions about the product must be neutral and true
- Try to understand the moods and reactions of others
- Try to convey what you want to say and understand what others want to say
If you want to have more information about Testing services and the software testing basics, please contact us!
———————————————————–
Lotus Quality Assurance (LQA)
Tel: (+84) 24-6660-7474
Email: [email protected]
Website: https://www.lotus-qa.com/