In this our new series, 4 things every tester should know, we will take you through the foundational knowledge of testing: Testing levels, Testing Types, Testing Processes and Principles of Testing.
We would like to contribute to the communities the take-away testing videos which are short but essential.
Hence, this series is named “Four Things Every Tester Should Know”, made for:
- Junior testers who are building foundational knowledge in software quality assurance and testing
- Senior testers who wants to revise their knowledge on testing
- Business users who want to have a high-level view of the testing industry


You can watch our video series here, or read the transcription below. Turn on subtitles for English, Japanese, Korean and Vietnamese.
The series will include the following topics:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1f9Ssis5SuE&list=PLI5JkQdCF-6ic2ceHiitDoIbYrZ1BYttG
Test levels
16 years ago, I came to know about some testing concepts and I think it’s very important.
Today, I want to share you one concept named “Testing Level”. So, let’s get started!
Have you ever heard about V-Model?
As you can see on our picture, there are 4 testing levels ordered from bottom to the top. Those are unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing.
Those are unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing.
Why do we need to distinguish those testing levels?
Because we can understand the specific objectives of each level you can integrate effectively using them to improve the qualities.
Following the timeline, we start with unit testing.
Unit testing, known as component testing,
is to verify the functional and non-functional behavior of the module in the system.
Normally the programmers do the Unit testing by isolating their module from the rest of the system.
They can do it manually or automatically by using a tool named Junit or Nunit.
The developer will base on detailed design to take the code,
data structure or the database in order to find out
if there are any data flow problems or any incorrect codes.
After finishing unit testing, we go to “Integration testing”
Integration testing is to verify the functional and non-functional interfaces
between components or systems of integration.
So, there are two types of integration.
First one is that component integration testing will be done by the programmer.
And system integration testing might be done by the independent testing team.
So, depending on each type, the input and the output,
and the system under test (SUT) might be differed.
But the objective seems to be same.
We focus on the integration between the component or the system.
The next step is system testing.
System testing focuses on the behavior and the capabilities
of a whole system or whole product as the end-to-end usage.
Independent testing team typically carry out system testing
and they will set up the test environment that is very similar to the production one.
They will produce the testing report which can be used
by stakeholders in order to make release decisions.
The typical defects could be missing the requirements or any incorrect functionalities of the system.
The last level is acceptance testing.
Acceptance testing is similar to the system testing
which will focus on the behavior and also the capabilities
of the whole system or the whole product.
But, it’s different from the system test.
It may produce information to assess
the system’s readiness for deployment and usage by the end-user.
Finding the bug is not the objective of acceptance test
because it will be too late if you find defects at this step.
The acceptance testing is the responsibility of
the customers, business user, product owner and also the operator of the system.
Normally, there are four common forms of the acceptance testing
including the user acceptance testing, the operational acceptance testing,
contractual and regulatory acceptance testing,
and the last one is the alpha and beta testing.
So, those are four important testing levels.
At the beginning of the project,
all stakeholders, including the product owner, the project manager and
also the quality assurance manager should sit together and
plan how to handle those four levels in the projects.
To ensure that, the product and software will meet the business needs and also the user requirement.
Otherwise, the product or the system will be NOT fit to use.
So if you want to see more videos, please subscribe to us.
Also, hit on the bell to receive the notification.
Thank you for watching and see you soon!
—
Testing types
A testing types are groups of test activities which are based on specific testing objectives. We could have different aspects to distinguish the different testing types.
For example, following the Quality Characteristic aspect , we could have Functional testing and Non-functional testing. Following the testing method, we could have Whitebox, Greybox, Blackbox testing or Manual/automated testing. Following the testing environment, we could have the alpha, beta and staging testing and so on.
In this video, let’s distinguish just based on the quality characteristic aspect.
So, what is Software Quality Characteristics? Testers need to verify if the software has good quality or not, hence it is necessary to understand how to define the quality.
ISO/IEC 25010 is an international standard which is issued by ISO(international standard organization) for the evaluation of software quality. It defines 8 main (quality) characteristics, namely: Functionality, Performance, Security, and also Compatibility, Reliability, Usability,Maintainability, Portability.
In this video, we will just explain some popular types.
Functional testing & Non-functional testing
First of all, Functional testing. It is a testing type which focused on the completeness, correctness and appropriateness of the software systems.
It can be done manually or automatically supported by many commercial and open source tools.
Meanwhile, Non-functional testing will focus on the “how well” of the system behaves.
Performance testing
The second one is Performance. Performance testing is the process of determining the speed, responsiveness and also the stability of the software prograM, a computer, network, or device under the specific workload.
There are two main performance testing methods: load testing and stress testing.
- Load testing will help you to understand the behavior of a system under a specific load value.
- Stress testing will place a system under the higher-than-expected traffic loads to evaluate ‘how well’ of the system works above its expected capacity limits.
Security testing
And the next testing type is Security testing.
Security testing is to check if the software or the product is secured or not. It checks if the system is vulnerable to attacks or if someone can hack the system or login into the application without the authorization.
Some sources claim that security testing is a functional testing. Because it can be compliant with the old version ‘ ISO 9126’. But following the latest ‘ ISO 25010’ , security testing is a non-functional testing type and it is one of the quality characteristics separately.
Compatibility testing
And the last one I want to introduce today is about Compatibility Testing.
Compatibility Testing is a testing type to check if our software is capable in the different testing environments such as hardware, operating systems, applications, network, mobile or different versions of the software.
Because the compatibility testing will be repeated on the different environment, so it is highly recommended to be automated testing.
From my experience, Testing type is a significant knowledge that every tester should know in order to test correctly. When you are consulting clients and also proposing the quality assurance solution, test experts also should define the important quality characteristics for that specific system and also point out the relevant testing types.
So, that is a take away video about the testing types. It’s quite short but hopefully, it’s helpful.
—
Testing processes
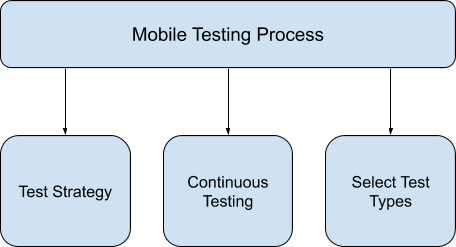
Continuing from the previous video about testing level and testing type, today I would like to introduce you another topic about testing process. Why do you need to know about the testing process? Because you will know what you need to do at each step and how to integrate testing into the development process. As you see in our picture, there are 5 steps when you do testing.
Test Planing and Test Control
Test planning is process to output the smart testing way. I often draw out an IMOC into one paper, and then document it later.
- I – the input means Test basic including the software specification, test requirement, software, etc. I plan How and When I can receive input.
- M – M is test Mechanism or how I will do the testing. I should think about the test strategy, schedule, and needed resources in order to do testing.
- O – Output of testing. Output is a test deliverable. For example, the test result, the test log, and bug report. I will plan of who I need to send the report to, and in which kind of format.
- C – Test constraint. One important test constraint is exit criteria. It is when I can stop testing.
Test control is the process to compare the actual progress and actual reason with the plan at the beginning. You also need to plan how you can control your progress, and how you can control the quality.
Test Analysis and Test Design
Test Analyzing is the process to analyze all of the test basics such as the test specification, requirement specification, and all additional documentation in order to define the test conditions. Test conditions could be a piece of functionality or anything you want to verify.
Test Designing is the step to break down the test condition into different test scenarios and cases. It is very important to use different test technique to cover all the possibilities of the test cases.
Test Implementation and Test Execution
In this step, the testers will combine the different test scenarios or test cases into the test procedures following business flows or into the test suite following the purposes of testing. Testers will prepare the test environment and make the automation script if it needs. After they get ready, the tester will execute the test cases, test suites, test procedures that they made before and log into the testing results. If they find bugs or any incidents, they will report it.
Evaluation and Reporting
At this step, we will evaluate whether the test implementation is satisfied with the test purpose by comparing test results with the exit criteria at the planning stage. We judge if we need additional testing or not and send reports to all stakeholders.
Test Closure
All of the Test closure activities are done when software is delivered. Tester will check all the deliverable, and archive test ware. Then, they can do any handover or needed training to the maintenance team (organization). And then, they evaluate how the testing went and learn the lessons for future projects.
Those are five steps of the testing process. If you have any suggestion, please comment below. Thank you for watching, and see you soon.
—
Principles of Testing
Continuing the series “Four things every tester needs to know about testing”, today will be the last topic named “7 Principles of testing”. We hope that the series of the video will be helpful for testers, especially freshers. Also through this series of the video, the experienced testers can be reminded about the basic but important knowledge. So, let’s get started!
Testing can only prove that the software has error
Through the testing, we can find the bug and prove that the software has error. But we can not prove that the software has absolutely no error at all. Even in the absence of errors, we cannot claim that our software has no errors in the future.
Testing the entire pattern is impossible
Testing the entire pattern (combining all conditions of testing entry) is not possible, except for some extremely simple software. Instead of testing the whole system, testers will point out some risky modules to focus on. There are some testing techniques to support us to do that.
Testing should be involved as soon as possible
Testers should be involved in the project as soon as possible to find out the bug early. So, the correction cost will be reduced. Earlier testing, cheaper correction cost.
Defect Clustering – uneven distribution of errors
Most of the errors will be concentrated in some certain modules. It is like the 80-20 principle. So, the smart tester will spend time to analyze the most risky area to focus on.
The pesticides
Have you ever heard about it? The test cases are very similar to pesticides, and can not be used repetitively to eradicate insects during farming. It will over time lead to the insects developing resistance to the pesticide.
If you perform the test case multiple times, it will fail to find the errors. So, it is necessary to review and improve test cases frequently.
Testing depends on context
For different contexts, there will be different testing methods. For example, testing for the banking system will be differed from testing for the sales website; such as different quality characteristics, different testing types and different testing approaches.
“Bug zero” pitfalls
Please do not focus on creating the system without errors, but forget the initial requirements from customers and users. Software testing is not mere finding defects, but it also addresses if the software is fit with the requirement or not.
Those are 7 principles of testing. Please comment if you have any questions. Thank you very much for watching. Have a nice day.
If you like this series, you might also want to take a look at our series on Mobile testing and visit our Youtube channel.
Interested in our Testing Services?
Book a meeting with us now!