Software testing is an important part of the entire software development life cycle. Through the testing phase, software defects can be identified early and remedied before final product delivery. Therefore, many software development companies focus on building strict testing processes and investing in in-house testing teams. This article will help you unlock the most common problems before diving in.
1. Why Software Testing is a MUST in every software development life cycle?
Software bugs can cause serious loss of money and people. Starbucks was forced to close about 60% of its stores in the United States and Canada, even serving free coffee because it was unable to process the transaction due to a software bug in its POS system. In 1994, China Airlines Airbus A300 crashed due to a software error, killing 264 people.
The examples above show that businesses can save up to millions per year, minimizing serious problems if they have a reliable and strict testing process. Besides, a software that is error-free and undergoes many rigorous quality checks will easily win the trust and satisfaction of customers; bring efficiency in both cost, security, as well as sustainable development.
2. How many types of Software testing?
Based on different criteria, we can classify Testing in many ways including:
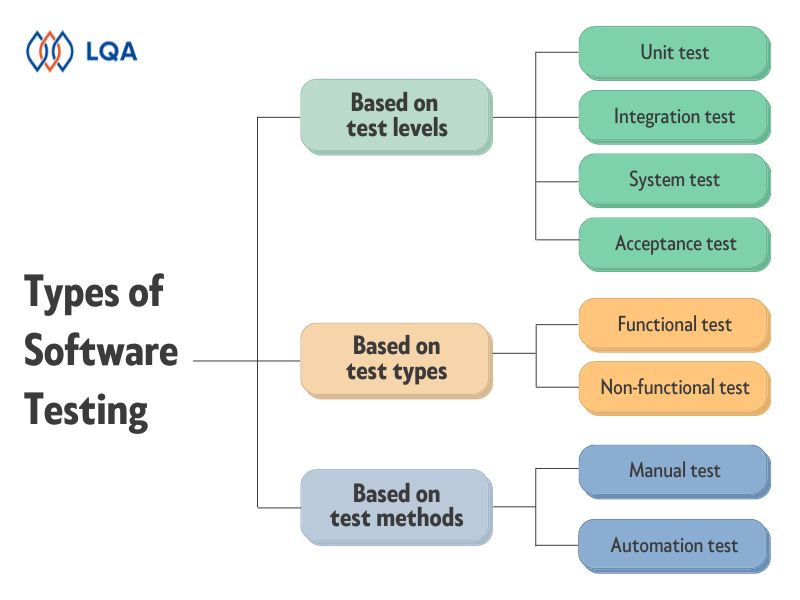
How many types of software testing?
a. According to test levels
- Unit testing: the process of testing corrections on an individual unit or component to assure that they work properly on their own. Unit testing is important because it enables us to find more defects at the unit test level, reduce wasted tests, and speed up testing strategies.
- Integration tests: a level of software testing where two or more modules of an application are logically grouped and tested as a whole. The focus of this type is to search for the defect in communication, interface, and data flow among modules. A top-down or Bottom-up approach is used while integrating modules into the whole system. This type of testing is done by integrating modules of a system or between systems.
- System Testing: a level of software testing that validates the complete and fully integrated software product. The purpose is to evaluate the end-to-end system specifications. Usually, the software is only one element of a larger computer-based system. Ultimately, the software is interfaced with other software/hardware systems. System Testing is defined as a series of different tests whose sole purpose is to exercise the full computer-based system.
- Acceptance testing: ensures that the end-user (customers) can achieve the goals set in the business requirements, which determines whether the software is acceptable for delivery or not. It is also known as user acceptance testing (UAT). Acceptance testing is a type of testing where the client/business/customer test the software with real-time business scenarios. The client accepts the software only when all the features and functionalities work as expected. This is the last phase of testing, after which the software goes into production. This is also called User Acceptance Testing (UAT).
b. According to test types
- Functional testing: a type of testing which verifies that each function of the software application operates in conformance with the requirement specification.
- Non-functional testing: a type of testing to check non-functional aspects (performance, usability, reliability, etc.) of a software application.
c. According to test methods
- Automation testing: a testing technique utilizing tools and test scripts to automate testing efforts. In other words, specified and customized tools are implemented in the testing process instead of solely manual forces.
- Manual testing: the technique in which a tester/a QA executes the whole testing process manually, from writing test cases to implementing them. In manual testing, QA analysts carry out tests one-by-one in an individual manner to find bugs, glitches and key feature issues prior to the software application’s launch. As part of this process, test cases and summary error reports are developed without any automation tools.
3. Is Automation Testing the most popular and why?
Manual Testing has been the most popular method of the quality assurance process in general, yet it exposes some limitations that cause many businesses to become testing-ineffective.
Up until now, automated testing is considered a more innovative technique to boost the effectiveness, test coverage, and test execution speed in software testing. With this new “approach”, the testing process is expected to yield more test cases in a shorter amount of time and expand test coverage.
While it does not entirely exclude manual touch within the process, automation testing is a favorable solution for its cost-efficiency and limited human intervention. To put it in other words, automation testing requires manual efforts to make automation testing possible.
Is Automation Testing the most popular and why?
The 8 promising prospects of Automation Testing include:
- High yield of ROI
- Consistent regression testing
- Broad test coverage
- Accuracy and Reliability
- Faster pace
- Developers and Testers unburdened
- Reduce Human Intervention
- Records of measure quality metrics
>> Learn more about From Manual to Automation Testing: Why Even Bother?
4. Manual Testing vs. Automation Testing comparison, and when to use each method?
Manual testing is the traditional and fundamental test method in software testing. We often use the manual method to test new products or when we don’t have a clear understanding of the products or when the systems haven’t become stable yet.
Automation testing is considered a high-tech test method in comparison to manual one. We often use this test method to reduce resources and time consumed for testing a system that is stably functioning and we already clearly know about it.
You can find a more specific comparison between Manual Testing and Automation Testing in this infographic.
Manual Testing vs. Automation Testing comparison, and when to use each method?
The answer of whether you should choose automation testing or manual testing depends on your situation.
Choose manual test if:
- Your product is new and you don’t have experience with this kind of product before.
- The AUT (Application under test) changes frequently.
- You have a limited budget.
- You want to ensure user-friendliness in the product.
- You want to handle complex test cases.
- Your team doesn’t have the tech ability (for any reason) to set up and maintain automation.
And choose automation test if:
- There are repetitive tasks in a stable-functioning system and you want to reduce these tasks.
- When your system has frequent releases and you want to decrease test cycle time to speed up the processes.
- You have a great budget for building automation testing.
- You consider the test ability is needed in a long-term period.
- You want better transparency of testing activities. Statistics and graphs about the test process, performance, and error rates are explicitly indicated.
> Learn more about Which is the cost-effective solution for your firm?
5. Automotive test vs Automation test: Aren’t they the same?
Many people still misunderstand that Automotive testing is Automation testing. Therefore, to better understand Automotive testing, let’s distinguish those two concepts:
Automation testing – is a software testing method with an automated nature, precisely, the Tester only needs to write a piece of code or use some tools such as Selenium, Test Complete, and JMeter,… to run all the stages automatically, including entering information, clicking, checking results, comparing actual results with hypothetical results, etc., without having to perform manual operations over and over again.
Automotive testing – is the testing of embedded software written for embedded systems. Specifically, embedded software is software that is pre-installed by the device manufacturer into a product and that is utilized immediately with the electronic device without the need for the user or third-party installation. An Embedded system is a combination of hardware and software and here the software is embedded in the hardware.
Automotive test vs Automation test: Aren’t they the same?
6. What are the challenges and difficulties of building a software testing team and process?
High initial investment cost for human resources
According to Payscale, based on the latest updates on Jan 04 2022, the average salary for a Software Tester is $56,468.
However, the investment cost for a Software Tester Engineer does not just stop at salary, but also includes the cost of recruitment, training and other employee benefits. The IT industry is currently facing a shortage of human resources; therefore, recruitment becomes extremely competitive among businesses. Software testers have a high chance of job hopping when they find a company with better benefits and salary. Employers have to invest a lot of money and effort for headhunt services to successfully recruit a quality employee.
In addition, Software Testers at different levels also have different salaries range. Below is the salary range of a Software Tester from Entry level to Experienced.
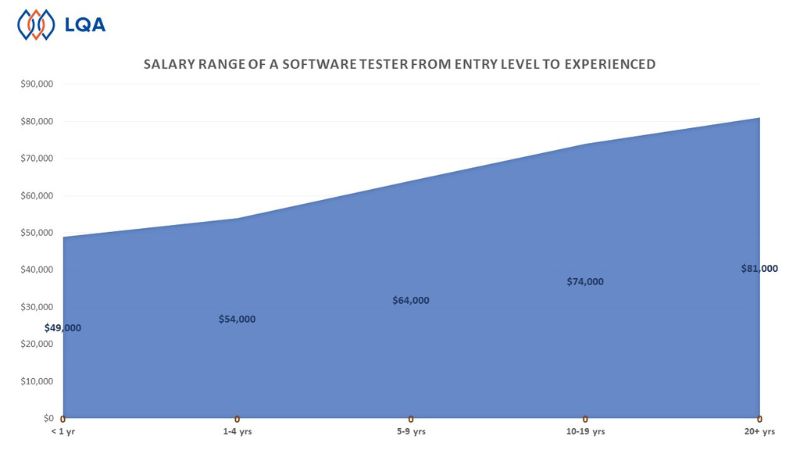
Software Testers salary range
The costs listed above are only calculated for one employee. Try to do a quick calculation, multiply this number by 5 or more if you want to build an in-house testing team.
High initial investment cost for testing tools
Besides the investment in human resources, businesses will have to prepare a budget for both facilities and testing tools. If it’s automation testing then you will only need to set up your computer and buy testing tools. But if it is an embedded test, the enterprise will have to invest in more complicated and expensive testing machines such as CANoe and CANat equipment, … Not to mention, when it comes to Integration and system testing, it requires set up for different test environments.
Bias in Software Testing: How Do Testers Miss Bugs?
According to Psychology Today, a bias is a tendency, inclination, or prejudice toward or against something or someone. Some biases are positive and helpful—like choosing to only eat foods that are considered healthy or staying away from someone who has knowingly caused harm. But biases are often based on stereotypes, rather than actual knowledge of an individual or circumstance. Whether positive or negative, such cognitive shortcuts can result in prejudgments that lead to rash decisions or discriminatory practices.
Bias in Software Testing: How Do Testers Miss Bugs?
One of the fundamentals of software testing; as referred to by the International Software Testing Quality Board (ISTQB); is that testing helps detection of defects. Taking into consideration that humans are an integral entity in software development, it is impossible to certify a 100% bug-free program when tests aren’t detecting any defects. Human testing detects and reduces the probability of undiscovered defects remaining in the software but even if no defects are found, it is not proof of perfection.
When the testers approach any testing, they are already influenced by their own biases – framing thoughts and judgments based on what to look for, where there would be potential defects coming up, who is developing it, the entire history of the program etc., and the list goes on.
7. In-House Software Testing vs. Outsourcing: What should you choose?
For the above challenges, many businesses choose to outsource software testing services. Because a flexible and quick team ramp-up/down on demands will bring benefits to businesses such as:
Cost-Effective and Time Efficient:
As mentioned above, effort, resources and investment costs for an in-house testing team are extremely expensive. Outsourcing a testing team will be the optimal choice to save the above investment costs. In particular, businesses can take advantage of low-cost labor when offshore outsourcing. For example, in Vietnam, the average salary of Software Test Engineer is $18633.55/year, 5 times lower than in the US and 6 times lower than in Japan (according to Salary expert data).
In addition, by outsourcing, your business can set up a testing team immediately, skipping the entire process of recruiting, training, setting up office equipment. An 24/7 available and flexible testing team that can ramp up or ramp down on demand. A team works independently, along with the in-house team to increase work efficiency and speed up time to market. Especially, when the demand for testing is huge due to continuously release, in-house QA team struggle to handle, offshore team can help optimize resource allocation. Your in-house team will not be overloaded and be able to focus on core business.

Cost-Effective and Time Efficient when Outsourcing Software Testing
Access to larger pool of Expertise and quicker transformation to another test method
When outsourcing to another country, your business will expand its talent network. This will also make it much easier to switch testing methods or types. No need to compete with domestic enterprises to hunt for candidates, no time to research and train new methods. If you want to move from manual testing to automation testing to optimize testing effort and speed up time to market, why not outsource it?
For example, in Vietnam today, IT resources are growing in both quantity and quality. According to the latest report of TopDev, Vietnam currently has 1.03M IT labor force and 62,000 graduated IT students/year. The Vietnamese government also has policies to support the development of the IT industry and facilitate international cooperation.

Software Testing outsourcing to Vietnam
In Vietnam, there are also leading testing companies, meeting international standards. LQA is an example when it becomes a silver partner of ISTQB (International Software Testing Qualifications Board).
No bias and Fresh perspective:
As shared above, one of the challenges and disadvantages of in-house testing teams is bias. To solve this problem, businesses can ask a 3rd party to cross-evaluate the quality of the product. From there, compare with the results of the in-house team to get the most objective result. Eliminating the trails of in-house testers and approaching fresh perspectives is the special benefit that offshore testing teams bring to businesses.
Below is a comparison table of the most basic criteria between Offshore Software Outsourcing Testing and In-house Software Testing. Businesses can rely on this assessment to choose the most optimal model for their needs at this time.
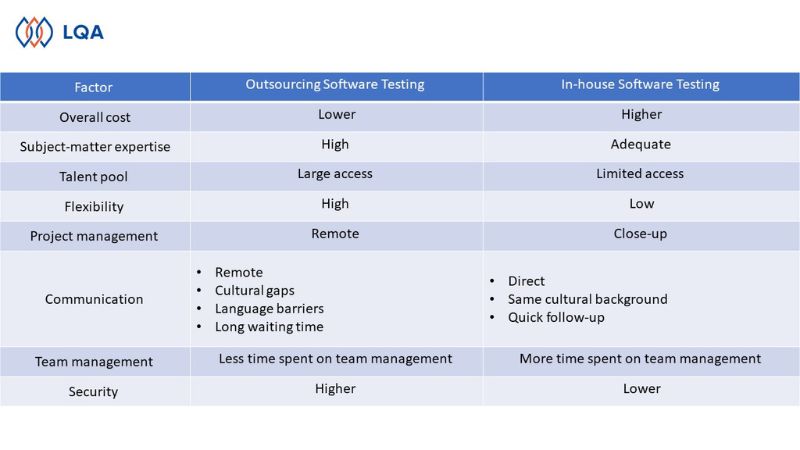
Offshore and In-house software testing comparison
However, every coin has two sides, outsourcing software testing also has some drawbacks, including language barrier and low security. Therefore, businesses must survey, learn and thoroughly evaluate the reputation of vendors before cooperating. Deeply aware of these concerns of businesses, LQA has always focused on improving the English skills of its personnel and always puts security first. With a closed quality management process and absolute security, LQA has been trusted by many large enterprises such as LG Electronics, Toshiba, Qualacomm, FPT, Baoviet,…
8. How many Offshore Software Testing Models are there and Which one is the Best-fit?
Once you have chosen a reputable vendor to outsource testing services, the next thing you need to pay special attention to is to agree on technical and engagement models from the very beginning. Working remotely with a team sitting on the other side of the globe will lead to miscommunication, misunderstandings in the process of cooperation. To limit this, businesses must agree on the process and way of working from the beginning. Below are the commonly used models and the cases where each specific model should be applied.
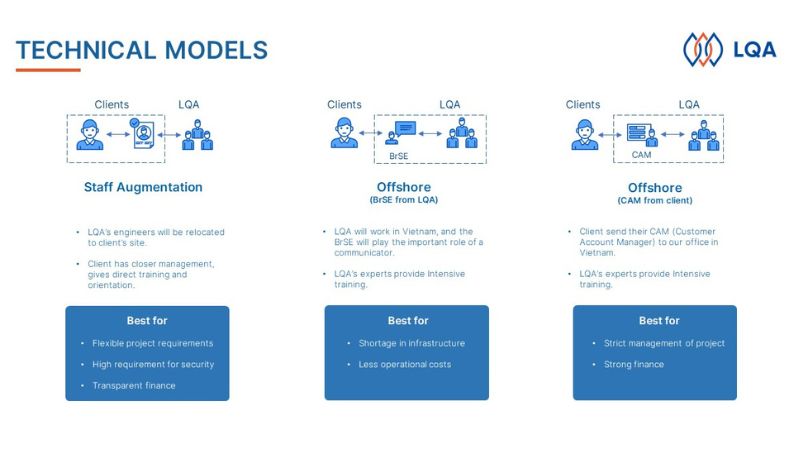
LQA software testing service technical model

LQA software testing service engagement model
Final Thoughts
LQA has listed and answered the above questions based on previous experience working with businesses. The above 8 questions are the 8 problems that many businesses worry the most when learning about Software Testing solutions. With thorough answers, LQA hopes to help you understand more about this field and find the best solution to optimize your business’ QA process and speed up time to market. If you are still struggling and need further professional advice, the LQA experts can help!
We, at Lotus QA, are just a contact form away:
Website: lotus-qa.com/
Tel: (+84) 24-6660-7474


